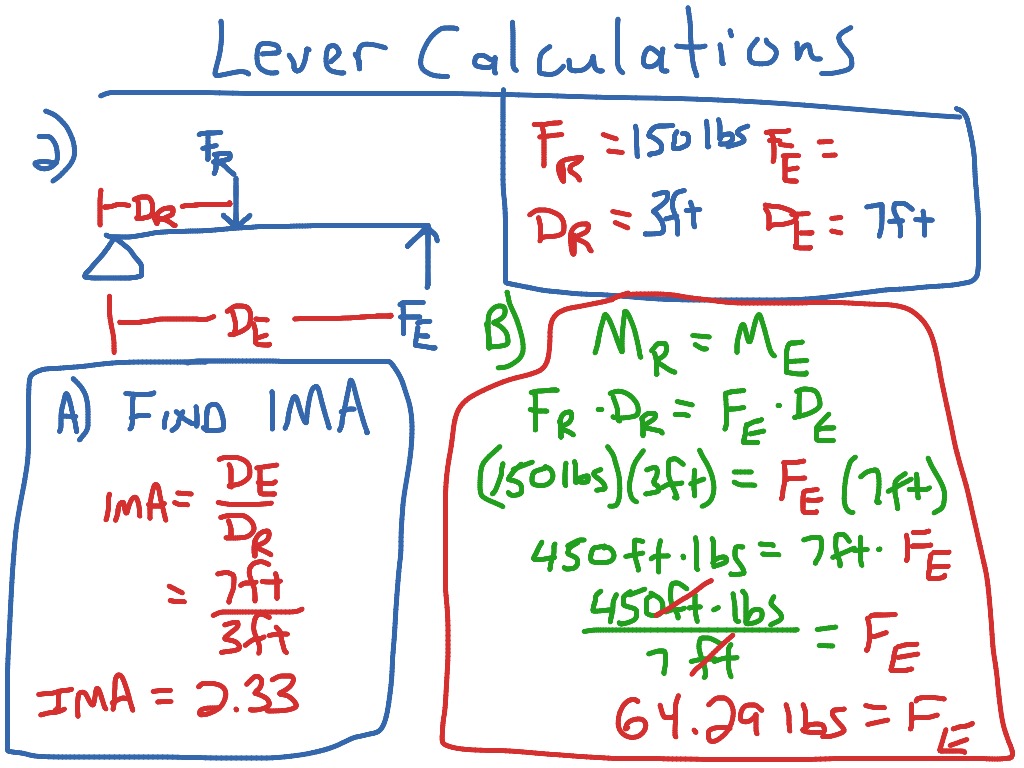
2nd class lever formula
2nd Class Lever Formula. About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy safety how youtube works test new features press copyright contact us creators. How do you calculate the mechanical advantage of a second class lever. The effort distance is the distance from the effort to the fulcrum. The 2nd class lever has the load in the middle the 3rd class lever has the effort in the middle an easy way to remember this is.
 Simple Force Level Calculator Case 3 Engineers Edge Www Engineersedge Com From engineersedge.com
Simple Force Level Calculator Case 3 Engineers Edge Www Engineersedge Com From engineersedge.com
F e 1 lb 1 ft 2 ft 0 5 lb example lever calculation with si units weight of 1 kg mass acting 1 m from the fulcrum. These types are based on the relative position of the fulcrum load and effort in the lever body. The three types of levers are as follows. This formula is used when you are given meters. Example second class order lever. It also sort of spells free.
In the picture to.
Example second class order lever. F e 1 lb 1 ft 2 ft 0 5 lb example lever calculation with si units weight of 1 kg mass acting 1 m from the fulcrum. In order for the above lever to be balanced the following equation must be satisfied. 1 answer ali ergin feb 9 2016 e l b a. The load arm load position is calculated from the law of the lever formula above. 1 first class lever or class i lever 2 second class lever or class ii lever and 3 third class lever or class iii lever.
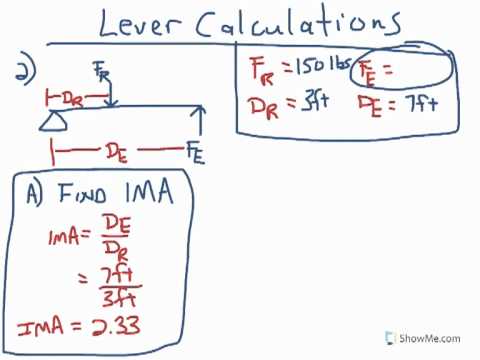 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The fulcrum and the load are located on the opposite sides of the lever. The fulcrum and the load are located on the opposite sides of the lever. In the second class lever the full length of the lever equals to the effort arm. Mechanical advantage of first class lever ma d 1 d 2 mechanical advantage of second class lever ma d 1 d 2 mechanical advantage of third class lever ma d 2 d 1 where ma mechanical advantage d 1 effort arm d 2 load arm related calculator. Example second class order lever.
 Source: engineersedge.com
Source: engineersedge.com
In order for the above lever to be balanced the following equation must be satisfied. These types are based on the relative position of the fulcrum load and effort in the lever body. In the second class lever the full length of the lever equals to the effort arm. The effort force at a distance of 2 ft from the fulcrum can be calculated as. Physics work and energy simple machines.
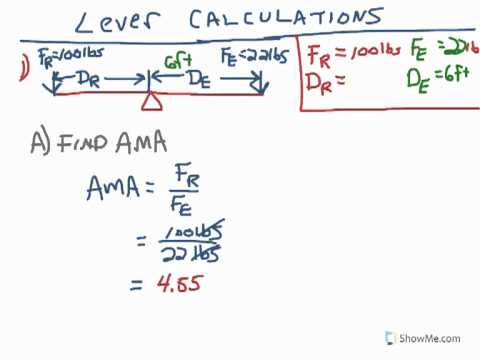 Source: m.youtube.com
Source: m.youtube.com
The 2nd class lever has the load in the middle the 3rd class lever has the effort in the middle an easy way to remember this is. F x l w x x. The three types of levers are as follows. Physics work and energy simple machines. It also sort of spells free.
 Source: scioly.org
Source: scioly.org
F e 1 lb 1 ft 2 ft 0 5 lb example lever calculation with si units weight of 1 kg mass acting 1 m from the fulcrum. A force weight of 1 pound is exerted at a distance of 1 ft from the fulcrum. A level where the load and effort force are located on the same side of the fulcrum is often characterized as a second class level mechanism. The fulcrum and the load are located on the opposite sides of the lever. Example second class order lever.
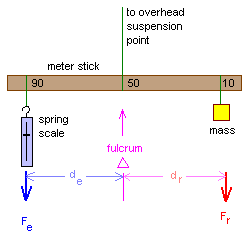 Source: comfsm.fm
Source: comfsm.fm
The effort distance is the distance from the effort to the fulcrum. F e 1 lb 1 ft 2 ft 0 5 lb example lever calculation with si units weight of 1 kg mass acting 1 m from the fulcrum. The effort is applied between the load and the fulcrum. What is the first class lever or class i lever. F x l w x x.
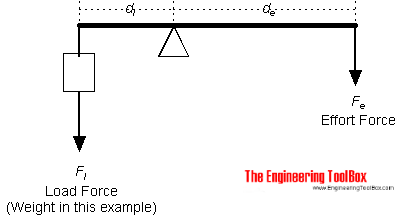 Source: engineeringtoolbox.com
Source: engineeringtoolbox.com
1 first class lever or class i lever 2 second class lever or class ii lever and 3 third class lever or class iii lever. Example second class order lever. Explain why the mechanical advantage of the class ii lever is always more than 1. This formula is used when you are given meters. The 2nd class lever has the load in the middle the 3rd class lever has the effort in the middle an easy way to remember this is.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The three types of levers are as follows. Example second class order lever. The effort force at a distance of 2 ft from the fulcrum can be calculated as. Distance between effort and fulcrum b distance between load and fulcrum e effort l load e a l b e l b a. In order for the above lever to be balanced the following equation must be satisfied.
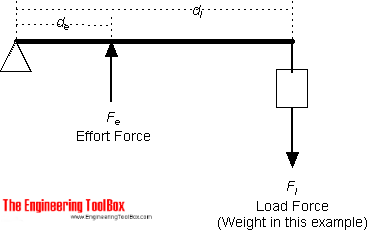 Source: engineeringtoolbox.com
Source: engineeringtoolbox.com
The effort force at a distance of 2 ft from the fulcrum can be calculated as. The effort is applied between the load and the fulcrum. In order for the above lever to be balanced the following equation must be satisfied. 1 first class lever or class i lever 2 second class lever or class ii lever and 3 third class lever or class iii lever. This lever mechanical advantage equation and calculator case 1 will determine the force required for equilibrium with the known forces and length.
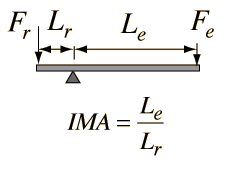 Source: www2.phy.ilstu.edu
Source: www2.phy.ilstu.edu
In the second class lever the full length of the lever equals to the effort arm. F w x x l. Explain why the mechanical advantage of the class ii lever is always more than 1. These types are based on the relative position of the fulcrum load and effort in the lever body. A 0 120 kg 50 0 cm long uniform bar has a small 0 055 kg mass glued to its left end and a small 0 110 kg mass.
 Source: translatorscafe.com
Source: translatorscafe.com
F 1 r 2 e 3 said f r e 1 2 3 it rhymes. F 1 r 2 e 3 said f r e 1 2 3 it rhymes. The load arm load position is calculated from the law of the lever formula above. Example second class order lever. Physics work and energy simple machines.
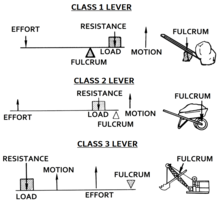 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
F x l w x x. The effort is applied between the load and the fulcrum. F x l w x x. A level where the load and effort force are located on the same side of the fulcrum is often characterized as a second class level mechanism. Distance between effort and fulcrum b distance between load and fulcrum e effort l load e a l b e l b a.
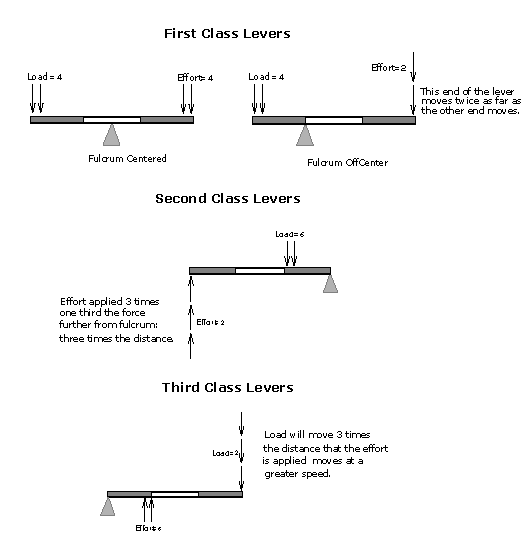 Source: www2.phy.ilstu.edu
Source: www2.phy.ilstu.edu
A 0 120 kg 50 0 cm long uniform bar has a small 0 055 kg mass glued to its left end and a small 0 110 kg mass. F e 1 lb 1 ft 2 ft 0 5 lb example lever calculation with si units weight of 1 kg mass acting 1 m from the fulcrum. What is the first class lever or class i lever. This formula is used when you are given meters. F 1 r 2 e 3 said f r e 1 2 3 it rhymes.
 Source: easycalculation.com
Source: easycalculation.com
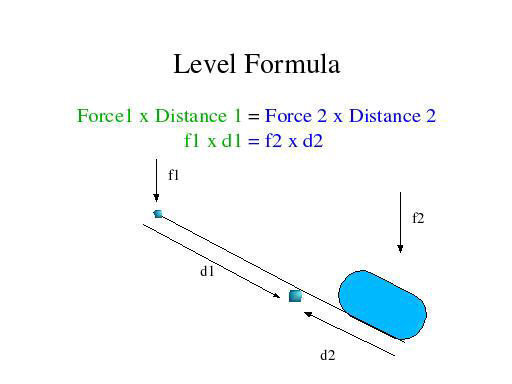
Distance between effort and fulcrum b distance between load and fulcrum e effort l load e a l b e l b a. A 0 120 kg 50 0 cm long uniform bar has a small 0 055 kg mass glued to its left end and a small 0 110 kg mass. In the picture to. It also sort of spells free. 1 answer ali ergin feb 9 2016 e l b a.
 Source: showme.com
Source: showme.com
F x l w x x. F e 1 lb 1 ft 2 ft 0 5 lb example lever calculation with si units weight of 1 kg mass acting 1 m from the fulcrum. In the picture to. Distance between effort and fulcrum b distance between load and fulcrum e effort l load e a l b e l b a. F 1 r 2 e 3 said f r e 1 2 3 it rhymes.
 Source: petervaldivia.com
Source: petervaldivia.com
The effort is applied between the load and the fulcrum. F e 1 lb 1 ft 2 ft 0 5 lb example lever calculation with si units weight of 1 kg mass acting 1 m from the fulcrum. Explain why the mechanical advantage of the class ii lever is always more than 1. What is the first class lever or class i lever. In order for the above lever to be balanced the following equation must be satisfied.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title 2nd class lever formula by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







