Ductility definition science
Ductility Definition Science. High ductility and very low hardness made gold easy to work using primitive techniques. Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations. Materials that are generally described as ductile include gold and. Ductility is the capacity of a material to deform permanently in response to stress.
 Difference Between Ductility And Malleability With Examples Youtube From youtube.com
Difference Between Ductility And Malleability With Examples Youtube From youtube.com
The ability of a material to have its shape changed as by being drawn out into wire or thread without losing strength or breaking when certain alloys are added to metal hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing defining a material s suitability for certain manufacturing operations and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload. Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material s amenability to drawing. In materials science ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Ductility definition the capacity to undergo a change of physical form without breaking. Ductility is the capacity of a material to deform permanently in response to stress.
Ductility is the capacity of a material to deform permanently in response to stress.
In materials science ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Materials that are generally described as ductile include gold and. Ductility is the capacity of a material to deform permanently in response to stress. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing defining a material s suitability for certain manufacturing operations and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload. The ability of a material to have its shape changed as by being drawn out into wire or thread without losing strength or breaking when certain alloys are added to metal hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility. Ductility definition the capacity to undergo a change of physical form without breaking.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
High ductility and very low hardness made gold easy to work using primitive techniques. The ability of a material to have its shape changed as by being drawn out into wire or thread without losing strength or breaking when certain alloys are added to metal hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility. Materials that are generally described as ductile include gold and. Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material s amenability to drawing. Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations.
 Source: nuclear-power.net
Source: nuclear-power.net
High ductility and very low hardness made gold easy to work using primitive techniques. Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing defining a material s suitability for certain manufacturing operations and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload. The ability of a material to have its shape changed as by being drawn out into wire or thread without losing strength or breaking when certain alloys are added to metal hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility. Ductility is the capacity of a material to deform permanently in response to stress.
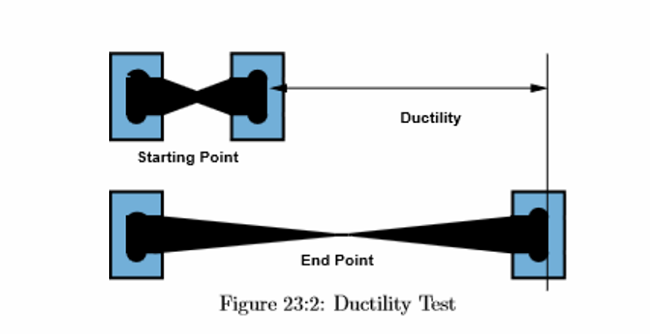 Source: e-education.psu.edu
Source: e-education.psu.edu
The ability of a material to have its shape changed as by being drawn out into wire or thread without losing strength or breaking when certain alloys are added to metal hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility. In materials science ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Materials that are generally described as ductile include gold and. Ductility is the capacity of a material to deform permanently in response to stress. Ductility definition the capacity to undergo a change of physical form without breaking.
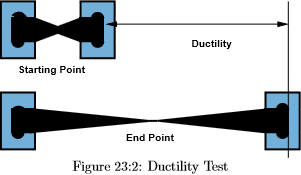 Source: e-education.psu.edu
Source: e-education.psu.edu
The ability of a material to have its shape changed as by being drawn out into wire or thread without losing strength or breaking when certain alloys are added to metal hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing defining a material s suitability for certain manufacturing operations and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload. Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations. In materials science ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Ductility is the capacity of a material to deform permanently in response to stress.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing defining a material s suitability for certain manufacturing operations and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload. Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material s amenability to drawing. Materials that are generally described as ductile include gold and. Ductility is the capacity of a material to deform permanently in response to stress.
Source: quora.com
Ductility definition the capacity to undergo a change of physical form without breaking. Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations. Ductility is the capacity of a material to deform permanently in response to stress. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing defining a material s suitability for certain manufacturing operations and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload. The ability of a material to have its shape changed as by being drawn out into wire or thread without losing strength or breaking when certain alloys are added to metal hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The quality or state of being ductile especially. Ductility definition the capacity to undergo a change of physical form without breaking. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing defining a material s suitability for certain manufacturing operations and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload. The ability of a material to have its shape changed as by being drawn out into wire or thread without losing strength or breaking when certain alloys are added to metal hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility. High ductility and very low hardness made gold easy to work using primitive techniques.
 Source: m.youtube.com
Source: m.youtube.com
Materials that are generally described as ductile include gold and. Materials that are generally described as ductile include gold and. High ductility and very low hardness made gold easy to work using primitive techniques. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing defining a material s suitability for certain manufacturing operations and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload. Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
In materials science ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Ductility is the capacity of a material to deform permanently in response to stress. In materials science ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material s amenability to drawing. High ductility and very low hardness made gold easy to work using primitive techniques.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Materials that are generally described as ductile include gold and. Materials that are generally described as ductile include gold and. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing defining a material s suitability for certain manufacturing operations and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload. Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material s amenability to drawing. Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations.
 Source: nuclear-power.net
Source: nuclear-power.net
High ductility and very low hardness made gold easy to work using primitive techniques. Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations. High ductility and very low hardness made gold easy to work using primitive techniques. Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations. The quality or state of being ductile especially.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
In materials science ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Materials that are generally described as ductile include gold and. Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material s amenability to drawing. The ability of a material to have its shape changed as by being drawn out into wire or thread without losing strength or breaking when certain alloys are added to metal hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility. In materials science ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations. The quality or state of being ductile especially. Materials that are generally described as ductile include gold and. In materials science ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Ductility definition the capacity to undergo a change of physical form without breaking.
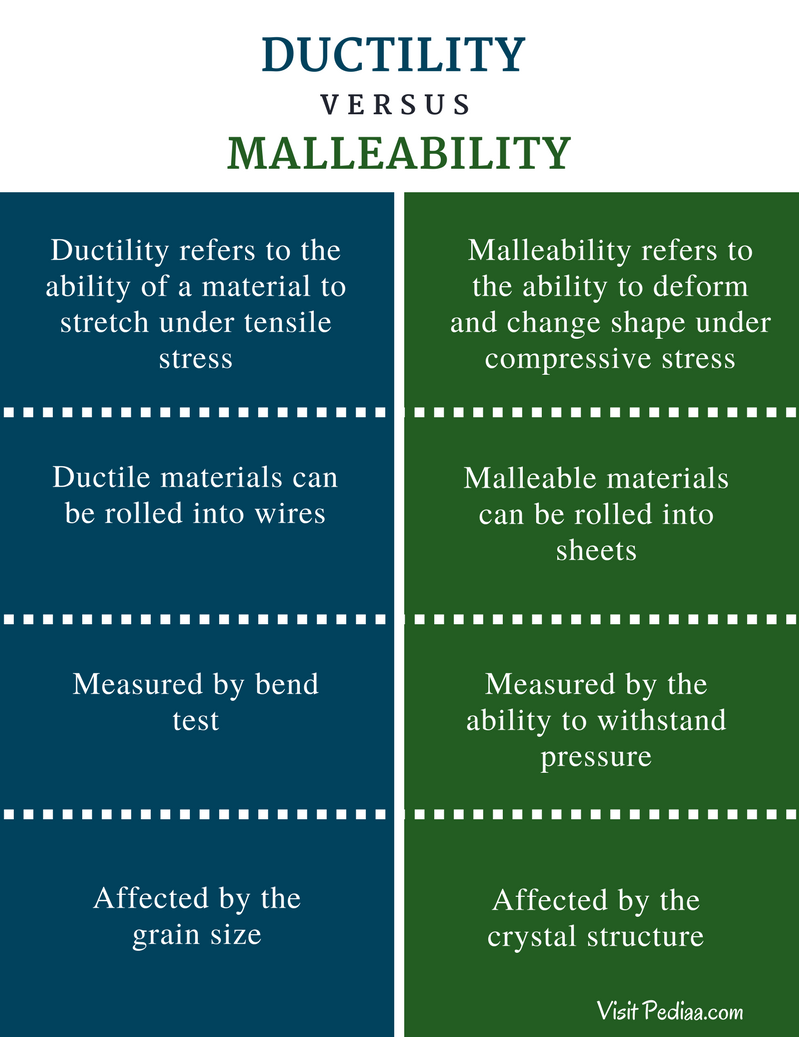 Source: pediaa.com
Source: pediaa.com
The ability of a material to have its shape changed as by being drawn out into wire or thread without losing strength or breaking when certain alloys are added to metal hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility. Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material s amenability to drawing. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing defining a material s suitability for certain manufacturing operations and its capacity to absorb mechanical overload. Ductility definition the capacity to undergo a change of physical form without breaking. High ductility and very low hardness made gold easy to work using primitive techniques.
 Source: e-education.psu.edu
Source: e-education.psu.edu
Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations. The quality or state of being ductile especially. In materials science ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure. Ductility is the capacity of a material to deform permanently in response to stress. Most common steels for example are quite ductile and hence can accommodate local stress concentrations.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title ductility definition science by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.