Eyeball parts anatomy
Eyeball Parts Anatomy. It extends forward and inward from the choroid coat and forms a ring inside the front of the eye. The gap between the sclera and the orbitals of the skull is filled with adipose tissue. The posterior pole of the eyeball is connected with the optic nerve cn ii which conveys the information from the retina to the brain. The extraocular muscles are attached to the white part of the eye called the sclera.
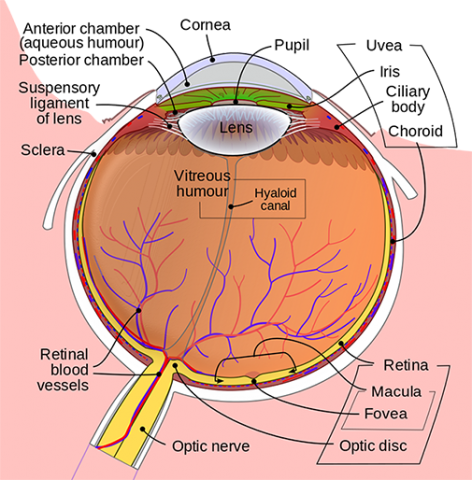 Anatomy Of The Eye Kellogg Eye Center Michigan Medicine From umkelloggeye.org
Anatomy Of The Eye Kellogg Eye Center Michigan Medicine From umkelloggeye.org
The sclera is the outermost layer and it gives a definite shape to the eye. Tears lubricate the eye and are made up of three layers. It is situated on an orbit of skull and is supplied by optic nerve. This is a strong layer of tissue that covers nearly the entire surface of the eyeball. Other internal structures include the lens retina and optic nerve. The posterior pole of the eyeball is connected with the optic nerve cn ii which conveys the information from the retina to the brain.
These structures work together to accomplish the task of receiving visual images and transmitting them to the brain.
The eye is the photo receptor organ. Anatomically the eyeball can be divided into three parts the fibrous vascular and inner layers. It makes up the outermost part of eye anatomy. These structures work together to accomplish the task of receiving visual images and transmitting them to the brain. The ciliary body is the thickest part of the middle layer of the wall of the eye. The eye is the photo receptor organ.
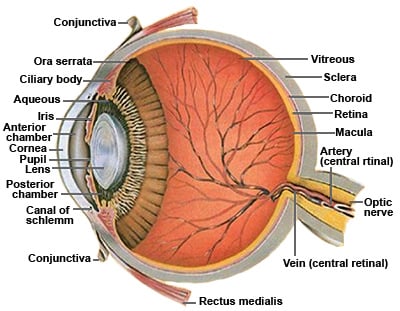 Source: mastereyeassociates.com
Source: mastereyeassociates.com
These structures work together to accomplish the task of receiving visual images and transmitting them to the brain. It lies in a bony cavity within the facial skeleton known as the bony orbit. The surface of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids are covered with a clear membrane called the conjunctiva. The outer fibrous layer maintains the shape of the eyeball and protects more fragile internal structure. The eyeball consists of three layers.
 Source: umkelloggeye.org
Source: umkelloggeye.org
Diagram of the different layers of the eyeball. A few of the visible parts include the the cornea iris pupil sclera and conjunctiva. Anatomically the eyeball can be divided into three parts the fibrous vascular and inner layers. The posterior pole of the eyeball is connected with the optic nerve cn ii which conveys the information from the retina to the brain. The extraocular muscles are attached to the white part of the eye called the sclera.
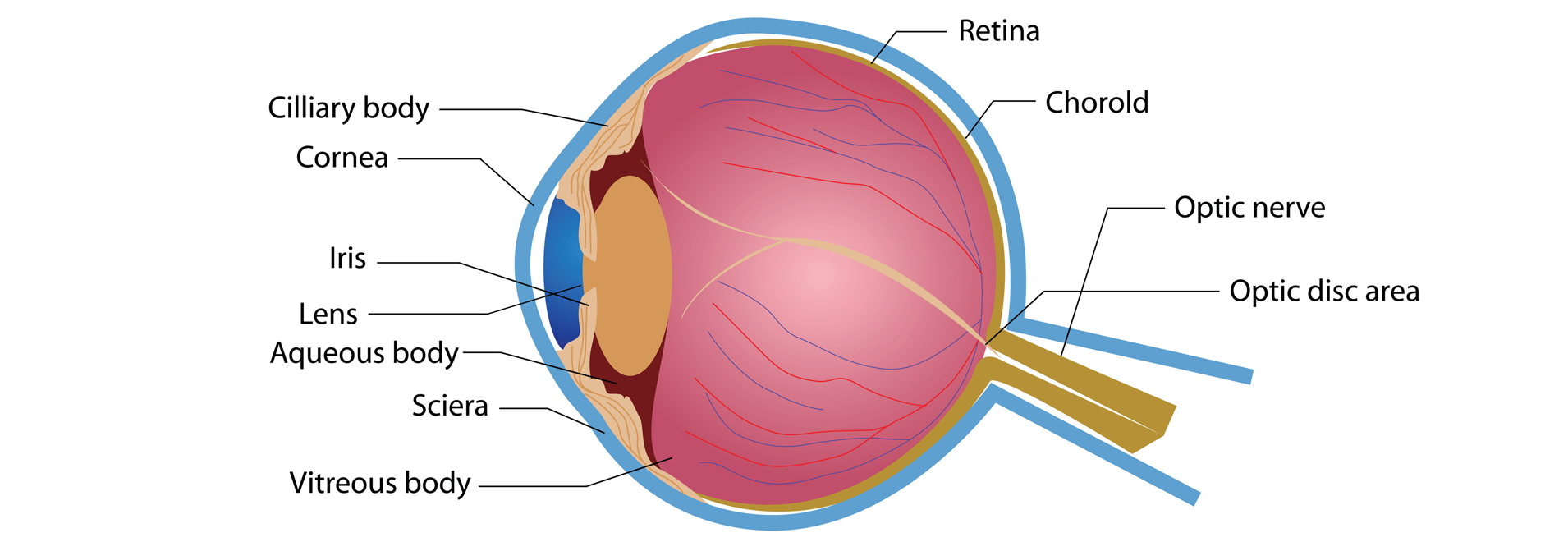 Source: eyecareproject.com
Source: eyecareproject.com
It is made of a dense strong fibrous wall consisting of the sclera that is 5 6th and the cornea that is anterior 1 6th of the eyeball. Anatomy parts and structure. Other internal structures include the lens retina and optic nerve. The ciliary body is the thickest part of the middle layer of the wall of the eye. Anatomically the eyeball can be divided into three parts the fibrous vascular and inner layers.
 Source: bellboothsirkka.com
Source: bellboothsirkka.com
The orbit is the bony eye socket of the skull. Causes loss of central vision as you get older. The orbit is formed by the cheekbone the forehead the temple and the side of the nose. The eyeball is a bilateral and spherical organ which houses the structures responsible for vision. Tears lubricate the eye and are made up of three layers.
 Source: glaucoma.org
Source: glaucoma.org
The gap between the sclera and the orbitals of the skull is filled with adipose tissue. The ciliary body is the thickest part of the middle layer of the wall of the eye. Causes loss of central vision as you get older. It extends forward and inward from the choroid coat and forms a ring inside the front of the eye. It lies in a bony cavity within the facial skeleton known as the bony orbit.
 Source: vision-and-eye-health.com
Source: vision-and-eye-health.com
Anatomy parts and structure. The orbit is the bony eye socket of the skull. This is a strong layer of tissue that covers nearly the entire surface of the eyeball. There are 6 sets of muscles attached to outer surface of eye ball which helps to rotate it in different direction. Other internal structures include the lens retina and optic nerve.
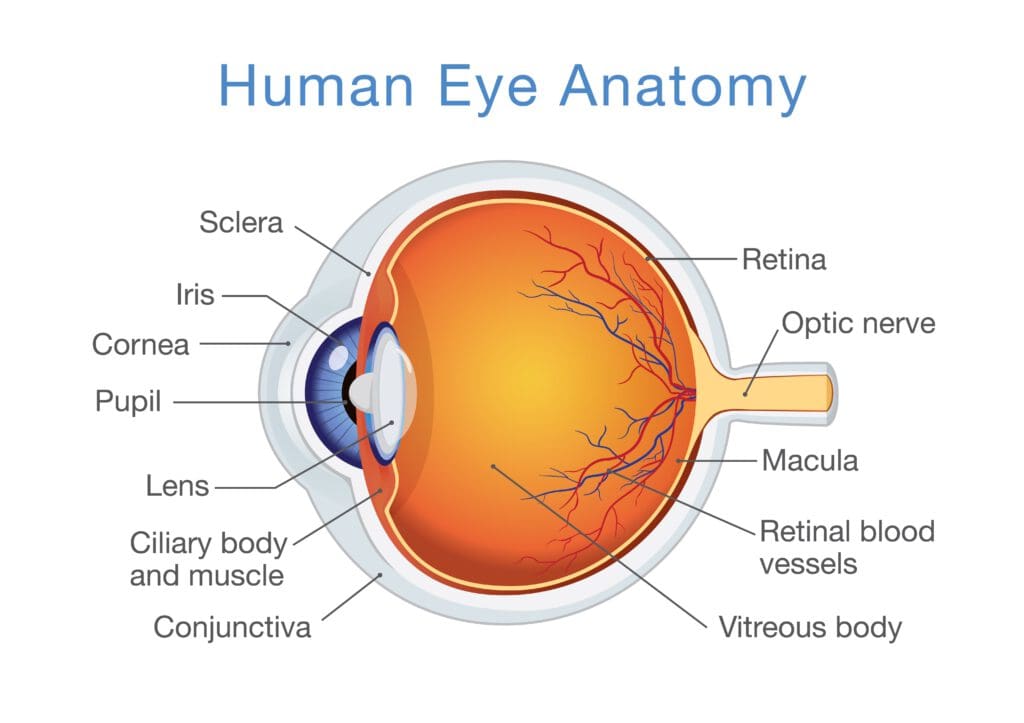 Source: nvisioncenters.com
Source: nvisioncenters.com
The orbit is the bony eye socket of the skull. The gap between the sclera and the orbitals of the skull is filled with adipose tissue. The wall of the eyeball is made up of three layers fibrous outer vascular muscular middle and sensorineural inner layers. The orbit is formed by the cheekbone the forehead the temple and the side of the nose. The sclera is the outermost layer and it gives a definite shape to the eye.
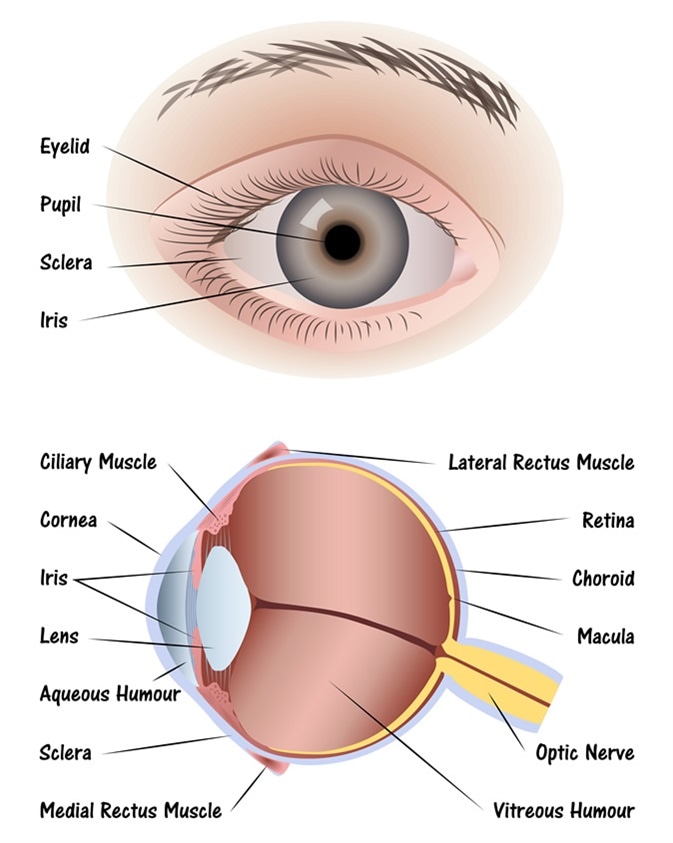 Source: news-medical.net
Source: news-medical.net
It is made of a dense strong fibrous wall consisting of the sclera that is 5 6th and the cornea that is anterior 1 6th of the eyeball. A few of the visible parts include the the cornea iris pupil sclera and conjunctiva. The eye is cushioned within the orbit by pads of fat. This is a strong layer of tissue that covers nearly the entire surface of the eyeball. It lies in a bony cavity within the facial skeleton known as the bony orbit.
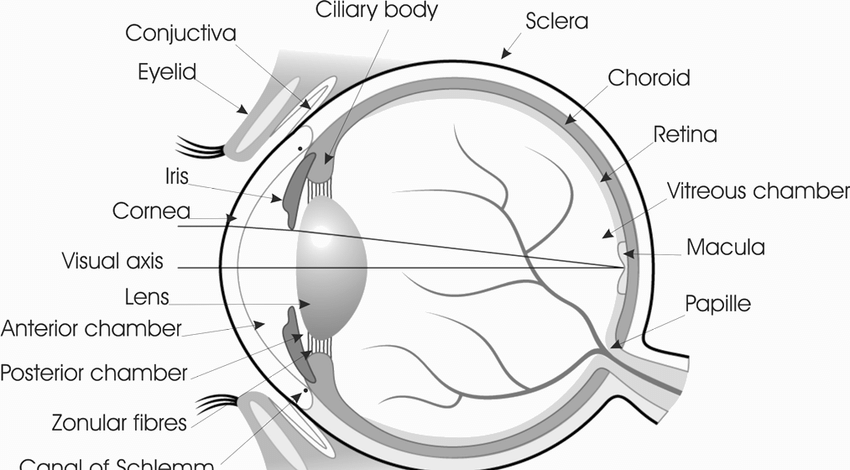 Source: lasikplus.com
Source: lasikplus.com
These structures work together to accomplish the task of receiving visual images and transmitting them to the brain. Tears lubricate the eye and are made up of three layers. Functionally the most important layer is the retina which receives the external visual stimuli. Human eye is spherical about 2 5 cm in diameter. In this article we shall consider the anatomy of the eyeball in detail and its clinical correlations.
 Source: aboutkidshealth.ca
Source: aboutkidshealth.ca
The posterior pole of the eyeball is connected with the optic nerve cn ii which conveys the information from the retina to the brain. The eyeball consists of three layers. Anatomically the eyeball can be divided into three parts the fibrous vascular and inner layers. The eye is cushioned within the orbit by pads of fat. The ciliary body is the thickest part of the middle layer of the wall of the eye.
 Source: ppoptometrists.co.za
Source: ppoptometrists.co.za
In this article we shall consider the anatomy of the eyeball in detail and its clinical correlations. Causes loss of central vision as you get older. The ciliary body is the thickest part of the middle layer of the wall of the eye. These structures work together to accomplish the task of receiving visual images and transmitting them to the brain. The eyeball is a bilateral and spherical organ which houses the structures responsible for vision.
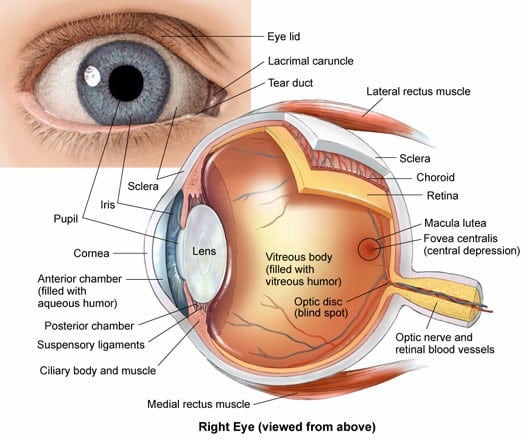 Source: columbiaeyeclinic.com
Source: columbiaeyeclinic.com
The posterior pole of the eyeball is connected with the optic nerve cn ii which conveys the information from the retina to the brain. Causes loss of central vision as you get older. The eye is the photo receptor organ. Functionally the most important layer is the retina which receives the external visual stimuli. The orbit is formed by the cheekbone the forehead the temple and the side of the nose.
 Source: macular.org
Source: macular.org
Anatomy parts and structure. These structures work together to accomplish the task of receiving visual images and transmitting them to the brain. This layer is made up of the sclera and cornea. A few of the visible parts include the the cornea iris pupil sclera and conjunctiva. The extraocular muscles are attached to the white part of the eye called the sclera.
 Source: medicinenet.com
Source: medicinenet.com
The eye is the photo receptor organ. It extends forward and inward from the choroid coat and forms a ring inside the front of the eye. Functionally the most important layer is the retina which receives the external visual stimuli. Human eye is spherical about 2 5 cm in diameter. The eye is the photo receptor organ.
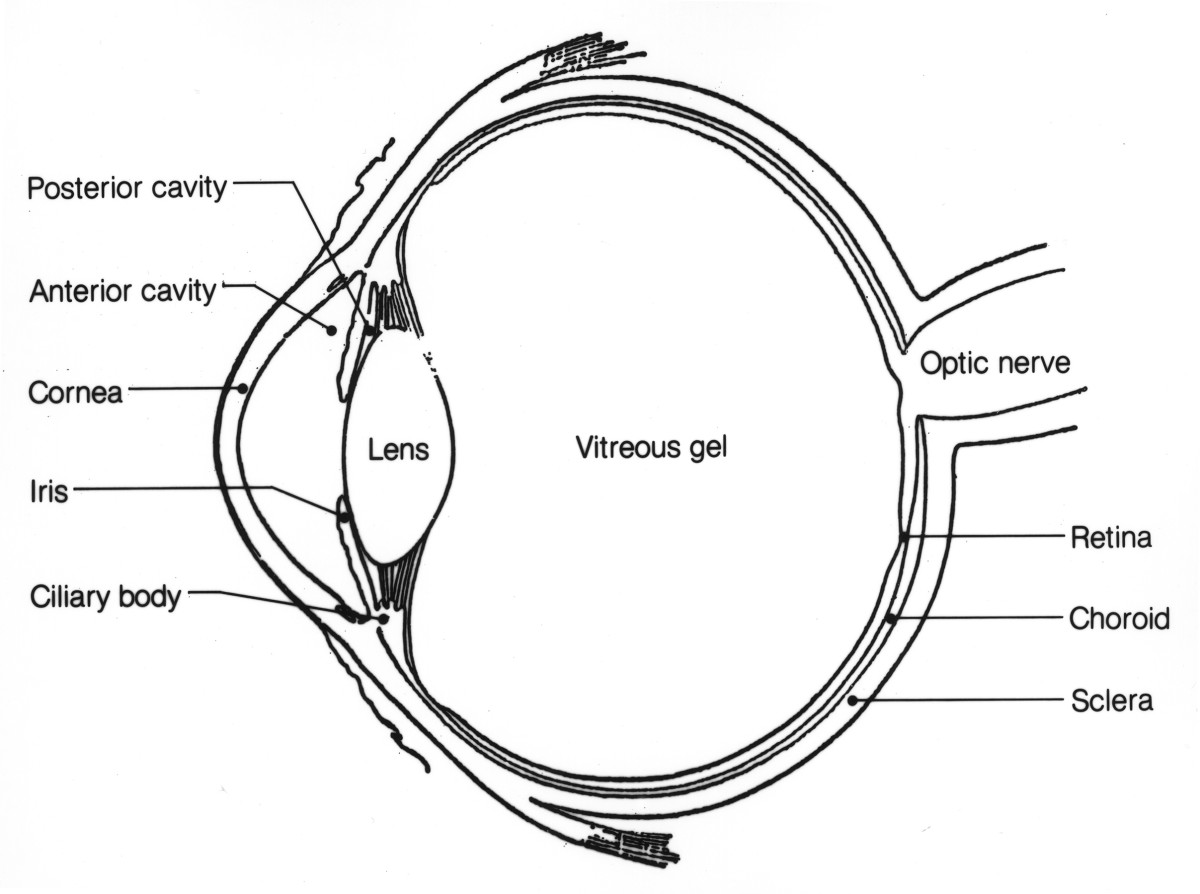 Source: owlcation.com
Source: owlcation.com
It lies in a bony cavity within the facial skeleton known as the bony orbit. Diagram of the different layers of the eyeball. The posterior pole of the eyeball is connected with the optic nerve cn ii which conveys the information from the retina to the brain. Anatomy parts and structure. In this article we shall consider the anatomy of the eyeball in detail and its clinical correlations.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title eyeball parts anatomy by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







