Fetal pig arteries
Fetal Pig Arteries. The artery which leaves the left ventricle and gives rise to the brachiocephalic trunk left subclavian artery and aorta. Large artery emerging from the right ventricle that branches into the pulmonary arteries that carry unoxygenated blood to the lungs. Urethra ovaries uterine tubes labia mesenteries testes epididymis vas deferens inguinal canal prostate gland etc. These structures are basically the same in the fetal pig and human.
 Zo250 Lab 3 Webpage From cals.ncsu.edu
Zo250 Lab 3 Webpage From cals.ncsu.edu
The hepatic artery leads to the liver. Fetal pig dissection of the lower arteries. Note the aorta where high pressure blood leaves the heart on its way to the systemic circulation. Haynoski points out the arteries and veins in a fetal pig. You may also see the right and left carotid arteries which supply blood to the head. The term innominate means nameless.
The term innominate means nameless.
Note the aorta where high pressure blood leaves the heart on its way to the systemic circulation. Fetal pig dissection of the lower arteries. Other branches were not significantly different between fetal pigs and humans including the acute marginal branch obtuse marginal branch and sinoatrial nodal artery. The term brachiocephalic refers to the vessels connections to the arm and head. In fetal pigs there was sometimes anastomosis 8 5 between the left and right conus branches as nutrient arteries of the pulmonary cone. Brachiocephalic vessels like humans the fetal pig has two brachiocephalic innominate veins but only one brachiocephalic artery.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Fetal pig dissection of the lower arteries. See this diagram for the fetal pig heart and the wikipedia heart article for some good diagrams of human heart anatomy. May not be visible. You may also see the right and left carotid arteries which supply blood to the head. The bicarotid trunk then splits into the right and left common carotid arteries.
 Source: usd388.k12.ks.us
Source: usd388.k12.ks.us
The bicarotid trunk then splits into the right and left common carotid arteries. Posterior vena cava carries blood to the heart. Coronary dominance was also similar. See this diagram for the fetal pig heart and the wikipedia heart article for some good diagrams of human heart anatomy. Haynoski points out the arteries and veins in a fetal pig.
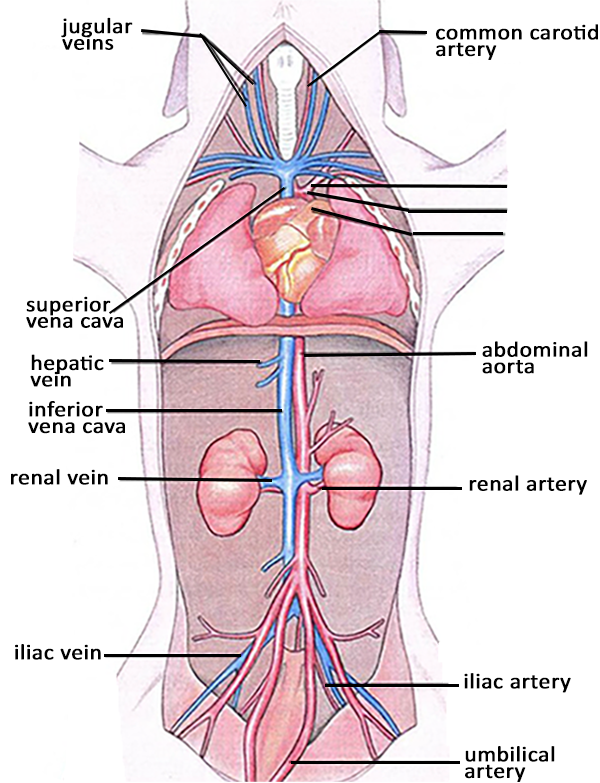 Source: biologycorner.com
Source: biologycorner.com
Posterior vena cava carries blood to the heart. The hepatic artery leads to the liver. Posterior vena cava carries blood to the heart. The term innominate means nameless. You may also see the right and left carotid arteries which supply blood to the head.
 Source: cals.ncsu.edu
Source: cals.ncsu.edu
The heart is surrounded by a pericardial sac. Large artery emerging from the right ventricle that branches into the pulmonary arteries that carry unoxygenated blood to the lungs. Haynoski points out the arteries and veins in a fetal pig. 63 71 of the fpdg fetal pig dissection guide. The circulation of blood in pig fetus is somewhat different.
 Source: cals.ncsu.edu
Source: cals.ncsu.edu
The hepatic artery leads to the liver. Posterior vena cava carries blood to the heart. The bicarotid trunk then splits into the right and left common carotid arteries. Haynoski points out the arteries and veins in a fetal pig. The heart is surrounded by a pericardial sac.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The term brachiocephalic refers to the vessels connections to the arm and head. The heart is surrounded by a pericardial sac. The term innominate means nameless. You may also see the right and left carotid arteries which supply blood to the head. The umbilical vein reaches the liver from where the blood enters the posterior vena cava through the passage ductus venosus.

Urethra ovaries uterine tubes labia mesenteries testes epididymis vas deferens inguinal canal prostate gland etc. The pig fetus receives oxygen rich blood from the placenta through the umbilical vein. Trace the abdominal aorta also called the dorsal aorta to the lower part of the body careful tweezing of the tissue will reveal several places where it branches though some of the arteries may have been cut when you removed organs of the digestive system. The artery which leaves the left ventricle and gives rise to the brachiocephalic trunk left subclavian artery and aorta. You may also see the right and left carotid arteries which supply blood to the head.
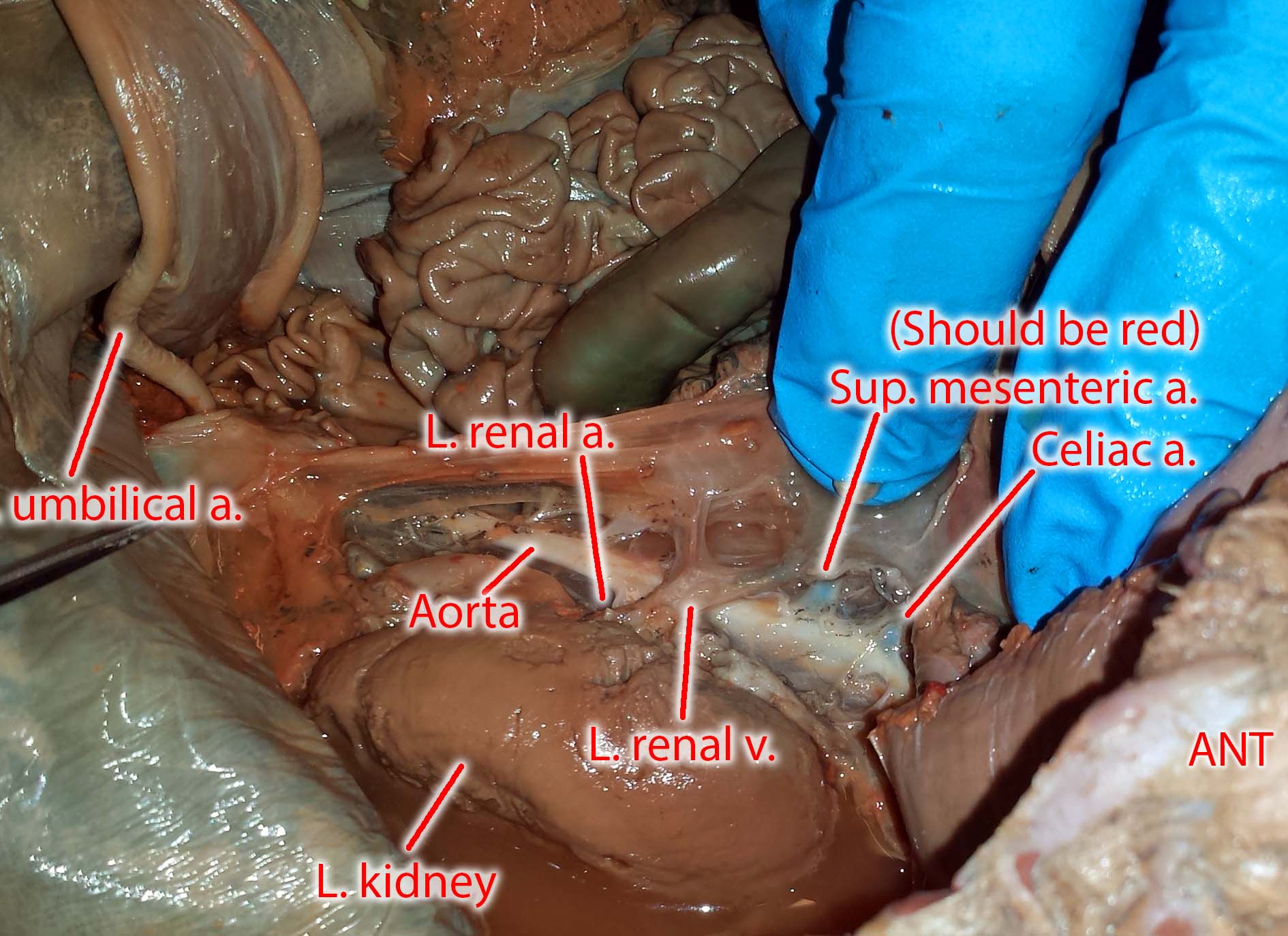 Source: blog.valdosta.edu
Source: blog.valdosta.edu
These structures are basically the same in the fetal pig and human. Trace the abdominal aorta also called the dorsal aorta to the lower part of the body careful tweezing of the tissue will reveal several places where it branches though some of the arteries may have been cut when you removed organs of the digestive system. The term brachiocephalic refers to the vessels connections to the arm and head. Urethra ovaries uterine tubes labia mesenteries testes epididymis vas deferens inguinal canal prostate gland etc. Haynoski points out the arteries and veins in a fetal pig.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Brachiocephalic vessels like humans the fetal pig has two brachiocephalic innominate veins but only one brachiocephalic artery. The pig fetus receives oxygen rich blood from the placenta through the umbilical vein. Bicarotid trunk in fetal pigs the brachiocephalic artery splits into the right subclavian artery and the bicarotid trunk. Posterior vena cava carries blood to the heart. The heart is surrounded by a pericardial sac.
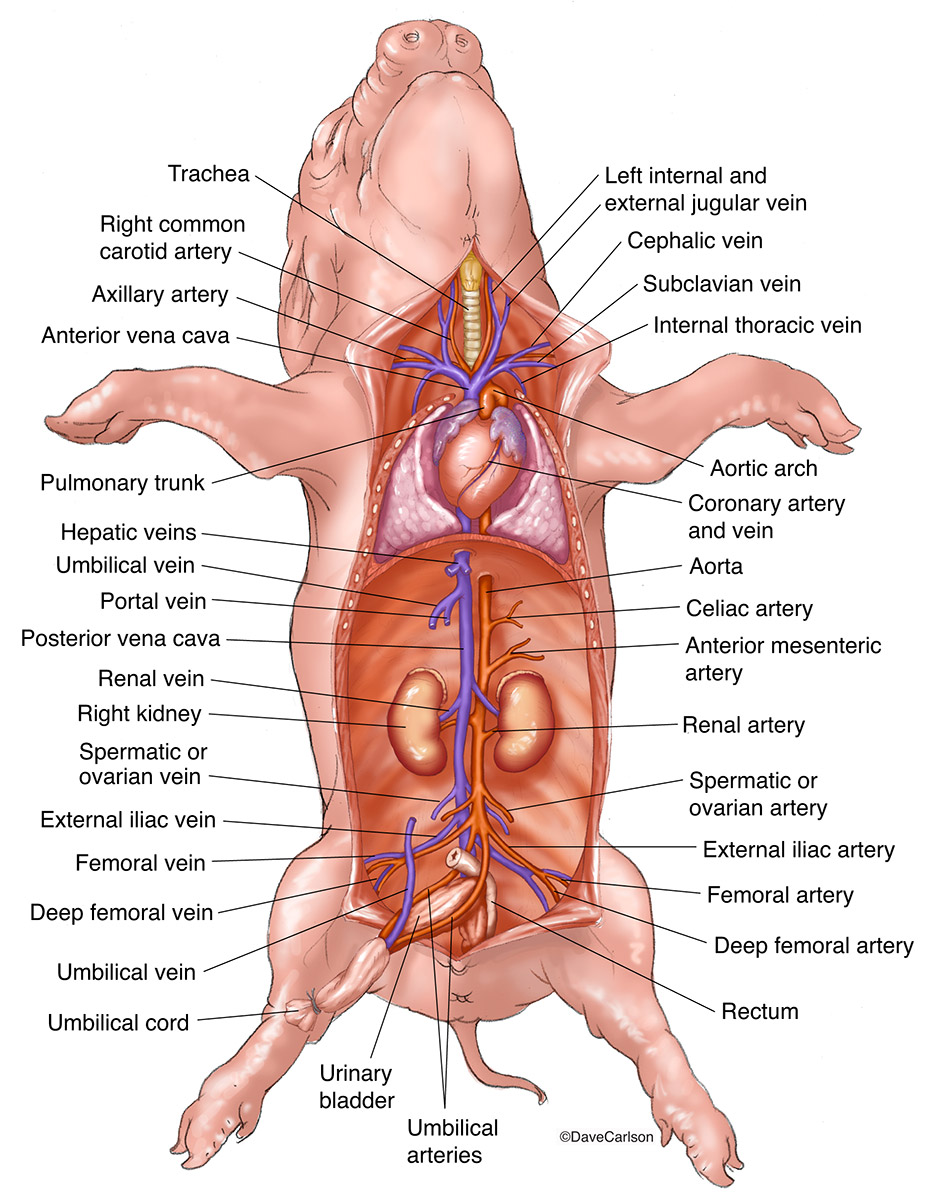 Source: carlsonstockart.com
Source: carlsonstockart.com
Trace the abdominal aorta also called the dorsal aorta to the lower part of the body careful tweezing of the tissue will reveal several places where it branches though some of the arteries may have been cut when you removed organs of the digestive system. You may also see the right and left carotid arteries which supply blood to the head. The pig fetus receives oxygen rich blood from the placenta through the umbilical vein. The circulation of blood in pig fetus is somewhat different. Other branches were not significantly different between fetal pigs and humans including the acute marginal branch obtuse marginal branch and sinoatrial nodal artery.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Other branches were not significantly different between fetal pigs and humans including the acute marginal branch obtuse marginal branch and sinoatrial nodal artery. The circulation of blood in pig fetus is somewhat different. Urethra ovaries uterine tubes labia mesenteries testes epididymis vas deferens inguinal canal prostate gland etc. The bicarotid trunk then splits into the right and left common carotid arteries. 63 71 of the fpdg fetal pig dissection guide.

Note the aorta where high pressure blood leaves the heart on its way to the systemic circulation. Urethra ovaries uterine tubes labia mesenteries testes epididymis vas deferens inguinal canal prostate gland etc. The umbilical vein reaches the liver from where the blood enters the posterior vena cava through the passage ductus venosus. These structures are basically the same in the fetal pig and human. The pig fetus receives oxygen rich blood from the placenta through the umbilical vein.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The umbilical vein reaches the liver from where the blood enters the posterior vena cava through the passage ductus venosus. The artery which leaves the left ventricle and gives rise to the brachiocephalic trunk left subclavian artery and aorta. These structures are basically the same in the fetal pig and human. Posterior vena cava carries blood to the heart. In fetal pigs there was sometimes anastomosis 8 5 between the left and right conus branches as nutrient arteries of the pulmonary cone.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
The hepatic artery leads to the liver. The term brachiocephalic refers to the vessels connections to the arm and head. The circulation of blood in pig fetus is somewhat different. Large artery emerging from the right ventricle that branches into the pulmonary arteries that carry unoxygenated blood to the lungs. Fetal pig dissection of the lower arteries.
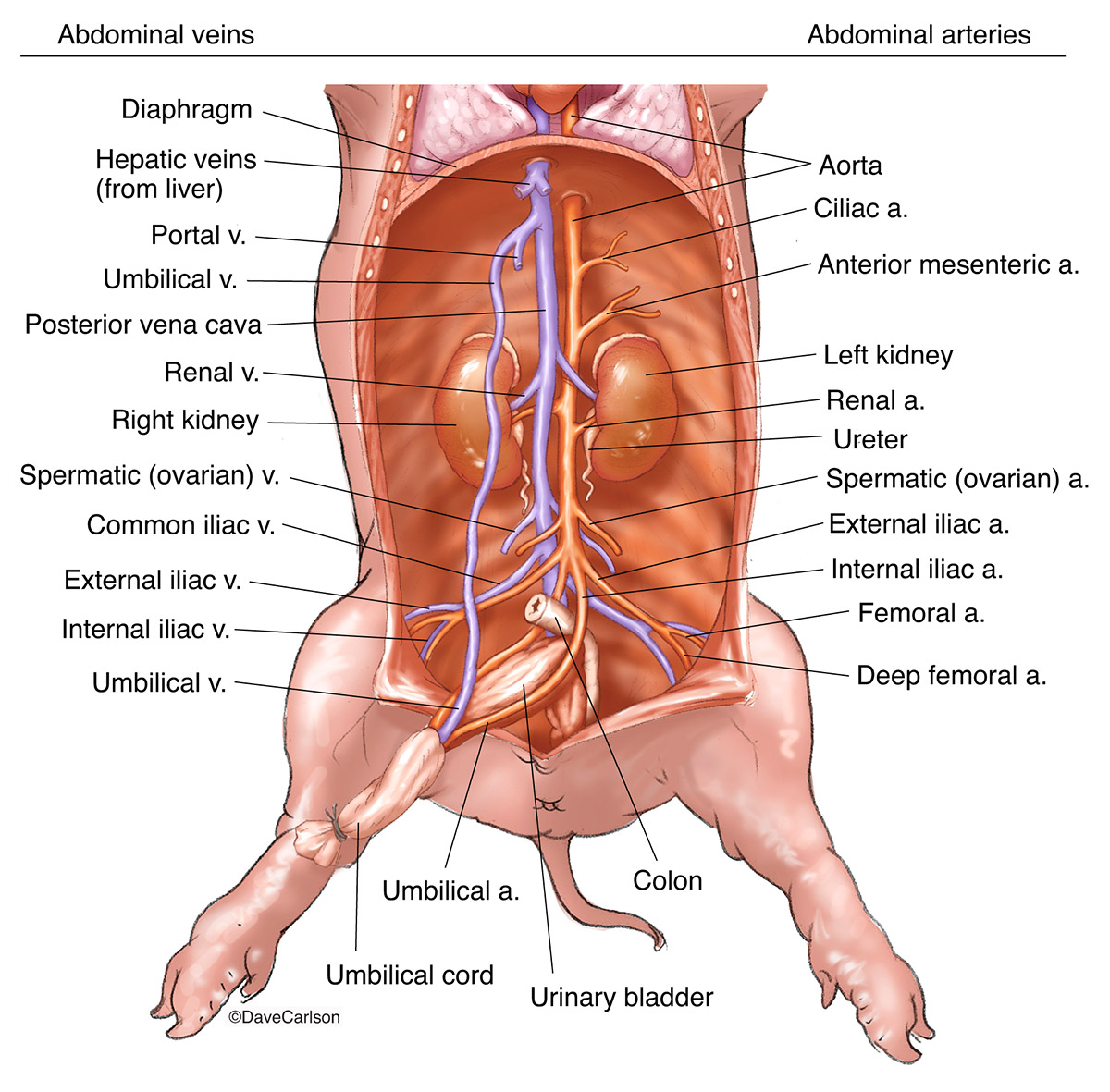 Source: carlsonstockart.com
Source: carlsonstockart.com
Note the aorta where high pressure blood leaves the heart on its way to the systemic circulation. The term brachiocephalic refers to the vessels connections to the arm and head. The pig fetus receives oxygen rich blood from the placenta through the umbilical vein. The circulation of blood in pig fetus is somewhat different. The artery which leaves the left ventricle and gives rise to the brachiocephalic trunk left subclavian artery and aorta.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title fetal pig arteries by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





