Fetal pig parts
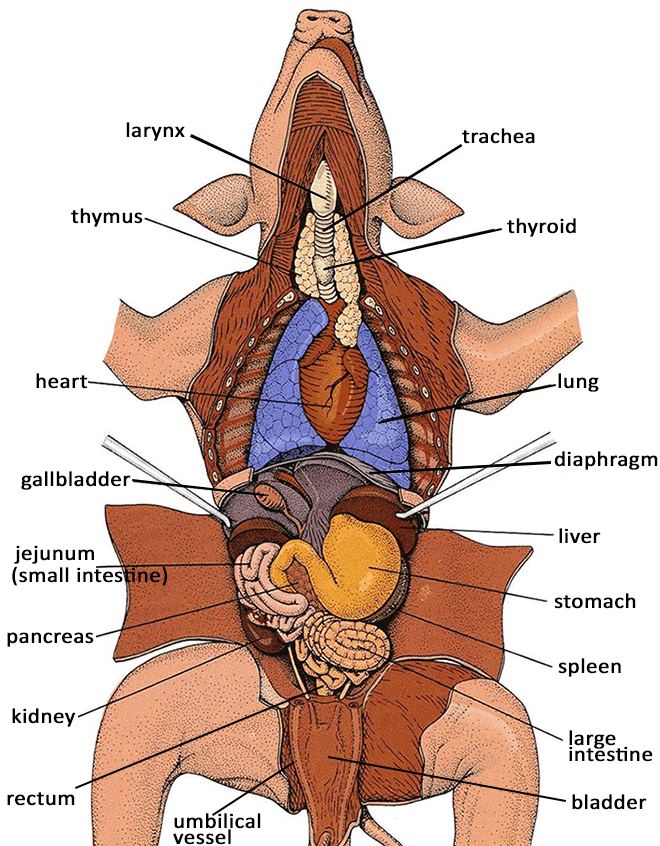
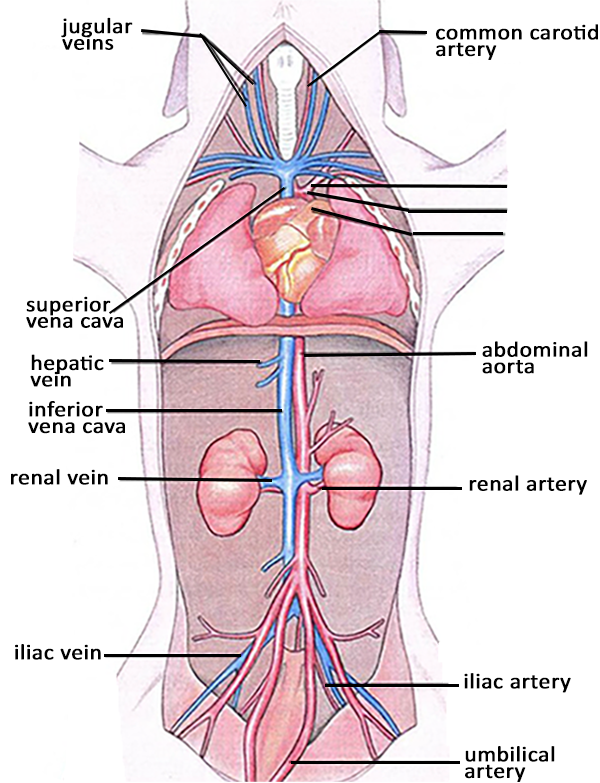
Fetal Pig Parts. It is opposite the dorsal side. Passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea. The pig in figure 1 is lying on its dorsal side. On the belly you will see the umbilical cord which connected the fetal pig to its mother s placenta.
Https Www Pearlandisd Org Cms Lib Tx01918186 Centricity Domain 1385 Fetal 20pig 20dissection 202019 20new Pdf From
Internal anatomy of fetal pig. Two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs. It is opposite the dorsal side. In addition you should study the two pre dissected specimens available in lab. Fetal pig being dissected showing the thoracic cavity including the rib cage the heart in the pericardium the lungs the diaphragm part of the liver and all the organs under the neck. Pushes air in and out of lungs by contracting.
Fetal pig that you can dissect with your group.
Determine if your specimen is male or female by looking closely at the umbilical cord area. The size of the fetal pig depends on the time allowed for the mother to gestate. Internal anatomy of a fetal pig emphasizing the cardiorespiratory digestive and urogenital systems male and female. Fetal pig that you can dissect with your group. Two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs. The pig in figure 1 below has its ventral side up.
 Source: br.pinterest.com
Source: br.pinterest.com
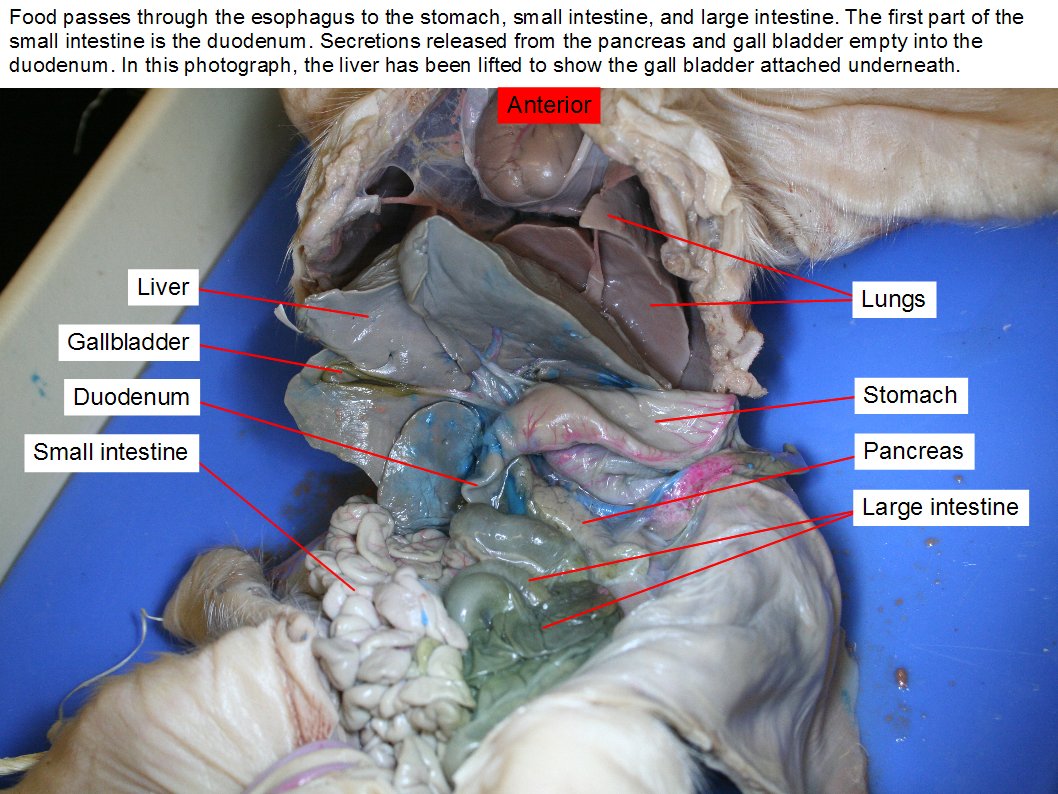
The liver is the largest organ of the abdominal cavity one of its many functions is to secrete bile which helps carry away waste and break down fats in the small intestine. Obtain a fetal pig and identify the structures listed in figure 1. The pig in figure 1 below has its ventral side up. Fetal pig being dissected showing the thoracic cavity including the rib cage the heart in the pericardium the lungs the diaphragm part of the liver and all the organs under the neck. Internal anatomy of fetal pig.
Source: biologyjunction.com
Ventral is the belly side. Recognize the structures labeled on the pictures on this page or listed in bold in the text. If the pig is male it will have a small urogenital opening immediately behind the umbilical cord. The size of the fetal pig depends on the time allowed for the mother to gestate. Use figures 1 4 below to identify its sex.
 Source: biologycorner.com
Source: biologycorner.com
The pig in figure 1 below has its ventral side up. It is opposite the dorsal side. Determine if your specimen is male or female by looking closely at the umbilical cord area. Pushes air in and out of lungs by contracting. Tube through which air moves.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Internal anatomy of fetal pig. Two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs. The gall bladder is a sac like organ that sores the bile secreted by the liver. Use figures 1 4 below to identify its sex. Obtain a fetal pig and identify the structures listed in figure 1.
 Source: biologycorner.com
Source: biologycorner.com
Internal anatomy of fetal pig. Internal anatomy of fetal pig. Obtain a fetal pig and identify the structures listed in figure 1. Use figures 1 4 below to identify its sex. The pig in figure 1 is lying on its dorsal side.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Tube through which air moves. Obtain a fetal pig and identify the structures listed in figure 1. Fetal pig being dissected showing the thoracic cavity including the rib cage the heart in the pericardium the lungs the diaphragm part of the liver and all the organs under the neck. It is opposite the dorsal side. The pig in figure 1 is lying on its dorsal side.
 Source: walmart.com
Source: walmart.com
In addition you should study the two pre dissected specimens available in lab. Pushes air in and out of lungs by contracting. Fetal pig that you can dissect with your group. On the belly you will see the umbilical cord which connected the fetal pig to its mother s placenta. Determine if your specimen is male or female by looking closely at the umbilical cord area.
 Source: lwhittie.tumblr.com
Source: lwhittie.tumblr.com
Passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea. On the belly you will see the umbilical cord which connected the fetal pig to its mother s placenta. The size of the fetal pig depends on the time allowed for the mother to gestate. Pushes air in and out of lungs by contracting. The liver is the largest organ of the abdominal cavity one of its many functions is to secrete bile which helps carry away waste and break down fats in the small intestine.
 Source: m.youtube.com
Source: m.youtube.com
It is opposite the dorsal side. On either side of the umbilical cord you may see mammary papillae little nipples that will turn into teats in female pigs. The size of the fetal pig depends on the time allowed for the mother to gestate. Passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea. Use figures 1 4 below to identify its sex.
Source:
The gall bladder is a sac like organ that sores the bile secreted by the liver. Use figures 1 4 below to identify its sex. The size of the fetal pig depends on the time allowed for the mother to gestate. On the belly you will see the umbilical cord which connected the fetal pig to its mother s placenta. Tube through which air moves.
Source:
If the pig is male it will have a small urogenital opening immediately behind the umbilical cord. Tube through which air moves. On either side of the umbilical cord you may see mammary papillae little nipples that will turn into teats in female pigs. The size of the fetal pig depends on the time allowed for the mother to gestate. Determine if your specimen is male or female by looking closely at the umbilical cord area.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Ventral is the belly side. Pushes air in and out of lungs by contracting. Passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea. Fetal pig that you can dissect with your group. In addition you should study the two pre dissected specimens available in lab.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs. The size of the fetal pig depends on the time allowed for the mother to gestate. In this lab you ll dissect a fetal pig to get a look at the anatomy of a mammal. If the pig is male it will have a small urogenital opening immediately behind the umbilical cord. Obtain a fetal pig and identify the structures listed in figure 1.
Source:
In this lab you ll dissect a fetal pig to get a look at the anatomy of a mammal. Pushes air in and out of lungs by contracting. In this lab you ll dissect a fetal pig to get a look at the anatomy of a mammal. If the pig is male it will have a small urogenital opening immediately behind the umbilical cord. Ventral is the belly side.
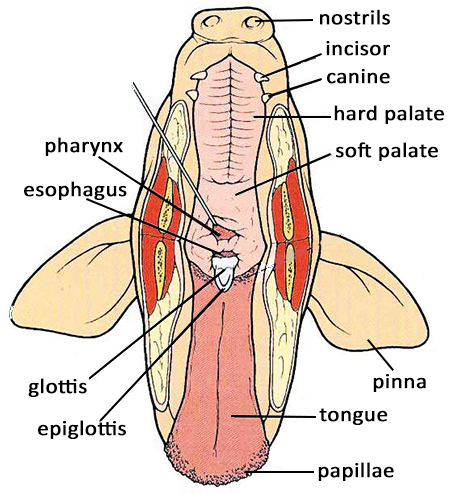 Source: biologycorner.com
Source: biologycorner.com
Use figures 1 4 below to identify its sex. Determine if your specimen is male or female by looking closely at the umbilical cord area. Recognize the structures labeled on the pictures on this page or listed in bold in the text. Tube through which air moves. Fetal pig being dissected showing the thoracic cavity including the rib cage the heart in the pericardium the lungs the diaphragm part of the liver and all the organs under the neck.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title fetal pig parts by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.