Newtons second laws of motion
Newtons Second Laws Of Motion. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object. According to newton s first law of motion if no net force is acting on a body at rest then the body remains at rest or if the body is moving will continue to move. Common newton s second law of motion examples is pushing trolly pulling the cart by applying force. Newton s second law helps us to explain why an object may speed up slow down or change.
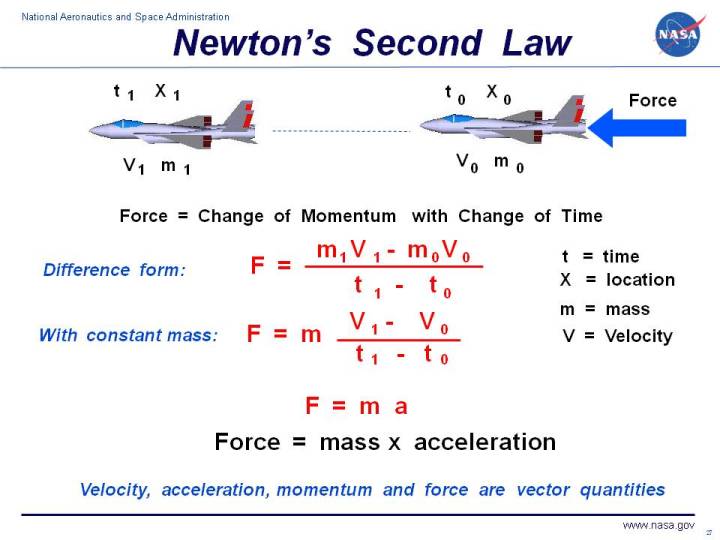 Newton S Second Law Of Motion From grc.nasa.gov
Newton S Second Law Of Motion From grc.nasa.gov
Newton s second law of motion states that the rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the applied force. The second law of motion describes what happens to the massive body when acted upon by an external force. Acceleration is directly proportional to the unbalanced force and is indirectly proportional to mass of the object. Since force is a vector we can write newton s second law as. In the second law the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. In the first law an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it.
In the second law the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration.
When an unbalanced force acts on an object the object will accelerate in the direction of the force. The 2nd law of motion states that the force acting on the body is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration. When an unbalanced force acts on an object the object will accelerate in the direction of the force. Newton s second law of motion. Common newton s second law of motion examples is pushing trolly pulling the cart by applying force. In the first law an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it.
 Source: brainly.in
Source: brainly.in
When an unbalanced force acts on an object the object will accelerate in the direction of the force. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object. The acceleration of an object depends directly upon the net force acting upon the object and inversely upon the mass of the object. Newton s second law of motion describes that when a force is applied to an object it produces acceleration in the object i e rate of change of velocity. Vec a dfrac sigma vec f m a mσf.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Newton s second law of motion. Vec a dfrac sigma vec f m a mσf. In the first law an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it. The direction of force f rightward the direction of friction force leftward the direction of friction force is opposite with the direction of object s motion. Newton s second law of motion describes that when a force is applied to an object it produces acceleration in the object i e rate of change of velocity.
 Source: physicsabout.com
Source: physicsabout.com
In the third law when two objects interact they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude and. Since force is a vector we can write newton s second law as. Newton s second law helps us to explain why an object may speed up slow down or change. A σ f m. Newton s second law of motion describes that when a force is applied to an object it produces acceleration in the object i e rate of change of velocity.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Newton s second law of motion. Newton s second law of motion. Common newton s second law of motion examples is pushing trolly pulling the cart by applying force. Newton s second law helps us to explain why an object may speed up slow down or change. Newton s second law of motion.
 Source: m.youtube.com
Source: m.youtube.com
The 2nd law of motion states that the force acting on the body is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration. F m a. In the first law an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it. According to newton s first law of motion if no net force is acting on a body at rest then the body remains at rest or if the body is moving will continue to move. Since force is a vector we can write newton s second law as.
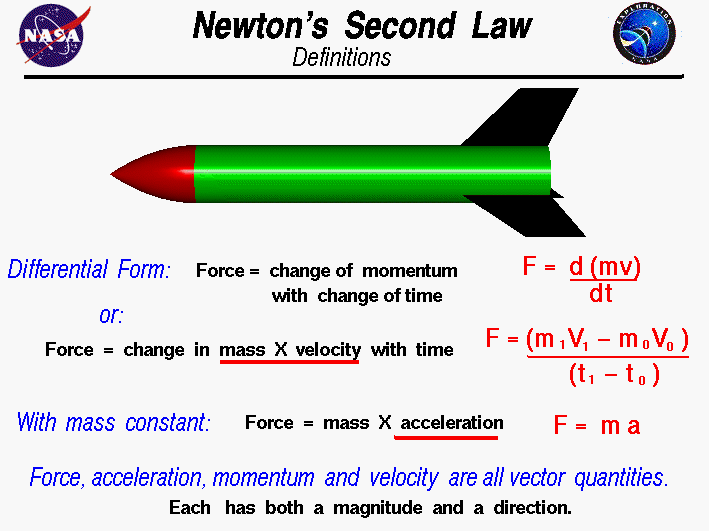 Source: grc.nasa.gov
Source: grc.nasa.gov
In the third law when two objects interact they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude and. Vec a dfrac sigma vec f m a mσf. The 2nd law of motion states that the force acting on the body is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration. Newton s second law of motion states that the rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the applied force. A with vector on top equals start fraction sigma f with vector on top divided by m end fraction.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Newton s second law of motion states that the rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the applied force. Common newton s second law of motion examples is pushing trolly pulling the cart by applying force. Newton s second law of motion pertains to the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are not balanced. In the second law the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. According to newton s first law of motion if no net force is acting on a body at rest then the body remains at rest or if the body is moving will continue to move.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The acceleration of an object depends directly upon the net force acting upon the object and inversely upon the mass of the object. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object. Newton s second law of motion. The second law of motion describes what happens to the massive body when acted upon by an external force. In the third law when two objects interact they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude and.
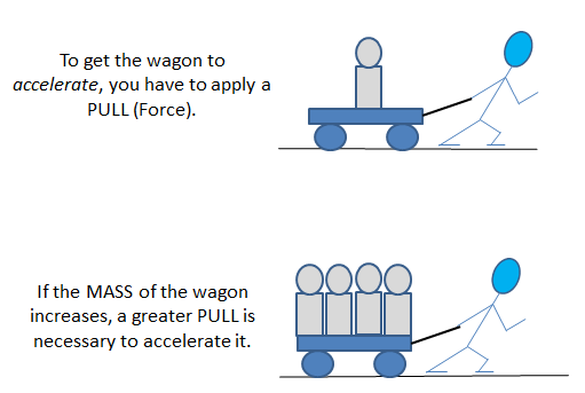 Source: physicalsciencetext.weebly.com
Source: physicalsciencetext.weebly.com
The 2nd law of motion states that the force acting on the body is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration. The direction of force f rightward the direction of friction force leftward the direction of friction force is opposite with the direction of object s motion. Newton s second law of motion describes that when a force is applied to an object it produces acceleration in the object i e rate of change of velocity. Common newton s second law of motion examples is pushing trolly pulling the cart by applying force. The acceleration of an object depends directly upon the net force acting upon the object and inversely upon the mass of the object.
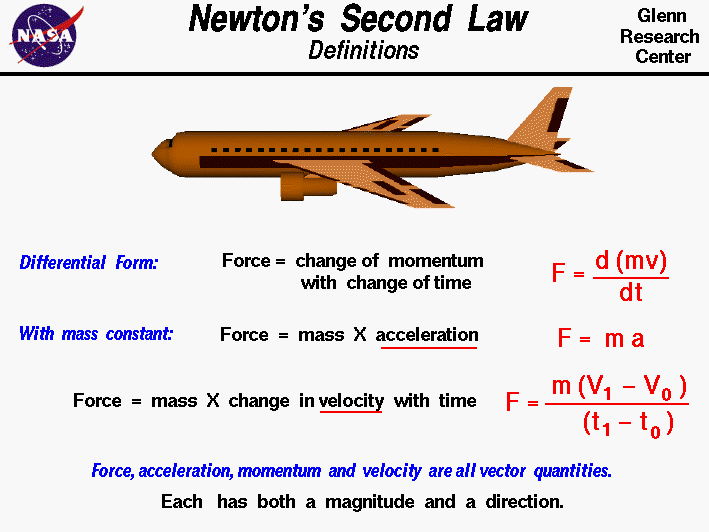 Source: grc.nasa.gov
Source: grc.nasa.gov
Common newton s second law of motion examples is pushing trolly pulling the cart by applying force. Newton s second law of motion. The direction of force f rightward the direction of friction force leftward the direction of friction force is opposite with the direction of object s motion. Newton s second law of motion pertains to the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are not balanced. According to newton s first law of motion if no net force is acting on a body at rest then the body remains at rest or if the body is moving will continue to move.
 Source: grc.nasa.gov
Source: grc.nasa.gov
Common newton s second law of motion examples is pushing trolly pulling the cart by applying force. Newton s second law of motion pertains to the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are not balanced. The direction of force f rightward the direction of friction force leftward the direction of friction force is opposite with the direction of object s motion. The second law of motion describes what happens to the massive body when acted upon by an external force. In the first law an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Newton s second law of motion states that the rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the applied force. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object. A σ f m. The acceleration of an object depends directly upon the net force acting upon the object and inversely upon the mass of the object. Newton s laws of motion relate an object s motion to the forces acting on it.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The second law of motion describes what happens to the massive body when acted upon by an external force. Newton s second law helps us to explain why an object may speed up slow down or change. Newton s second law of motion. F net force m mass a acceleration. Newton s second law of motion describes that when a force is applied to an object it produces acceleration in the object i e rate of change of velocity.
 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
Newton s second law of motion. Newton s second law of motion describes that when a force is applied to an object it produces acceleration in the object i e rate of change of velocity. Vec a dfrac sigma vec f m a mσf. The acceleration of an object depends directly upon the net force acting upon the object and inversely upon the mass of the object. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object.
 Source: justscience.in
Source: justscience.in
According to newton s first law of motion if no net force is acting on a body at rest then the body remains at rest or if the body is moving will continue to move. Newton s second law of motion pertains to the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are not balanced. Since force is a vector we can write newton s second law as. The acceleration of an object depends directly upon the net force acting upon the object and inversely upon the mass of the object. Newton s second law helps us to explain why an object may speed up slow down or change.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title newtons second laws of motion by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





