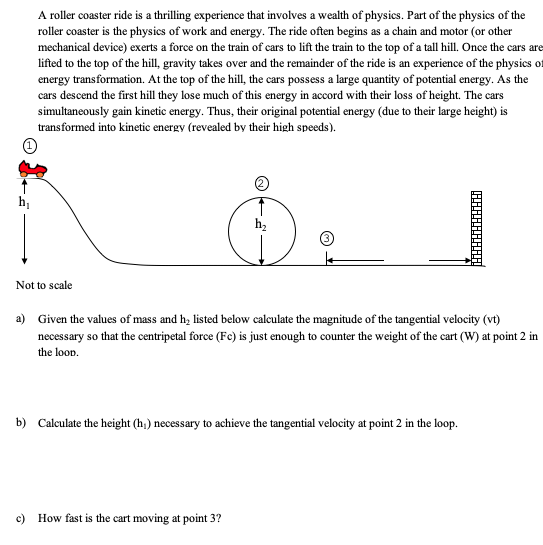
Roller coaster physics
Roller Coaster Physics. A roller coaster usually begins with a mechanical device such as a chain and motor which exerts a force on the car trains to lift them to the top of the hill. Roller coasters are almost entirely driven by different forces of inertia gravity and centripetal. Gravity plays a huge part in roller coaster physics. In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track.
Why Do We Ignore Normal Forces When Applying Conservation Of Energy To Roller Coasters Physics Stack Exchange From physics.stackexchange.com
In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track. A rightward moving roller coaster car gradually becomes an upward moving roller coaster car and a leftward moving roller coaster car then a downward moving roller coaster car. The forces experienced by the rider are constantly changing leading to feelings of joy in some riders and nausea in others. As the roller coaster cart passes through the clothoid loop one experiences acceleration based on two main factors. A roller coaster is a machine that uses gravity and inertia to send a train of cars along a winding track. Roller coasters are almost entirely driven by different forces of inertia gravity and centripetal.
A rightward moving roller coaster car gradually becomes an upward moving roller coaster car and a leftward moving roller coaster car then a downward moving roller coaster car.
In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track. A rightward moving roller coaster car gradually becomes an upward moving roller coaster car and a leftward moving roller coaster car then a downward moving roller coaster car. The physics of a roller coaster also involves work energy friction inertia and air resistance. As a coaster gets higher gravity can pull the cars down faster and faster to push them along the tracks. The basic principles of roller coaster mechanics have been known since 1865 and since then. Return to amusement park physics page.
 Source: worldsciencefestival.com
Source: worldsciencefestival.com
A rightward moving roller coaster car gradually becomes an upward moving roller coaster car and a leftward moving roller coaster car then a downward moving roller coaster car. The basic principles of roller coaster mechanics have been known since 1865 and since then. Gravity plays a huge part in roller coaster physics. Return to amusement park physics page. In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
A roller coaster usually begins with a mechanical device such as a chain and motor which exerts a force on the car trains to lift them to the top of the hill. A rightward moving roller coaster car gradually becomes an upward moving roller coaster car and a leftward moving roller coaster car then a downward moving roller coaster car. Roller coasters are almost entirely driven by different forces of inertia gravity and centripetal. Gravity plays a huge part in roller coaster physics. In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track.
 Source: rollercoasterphysics.webnode.com
Source: rollercoasterphysics.webnode.com
A rightward moving roller coaster car gradually becomes an upward moving roller coaster car and a leftward moving roller coaster car then a downward moving roller coaster car. In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track. As the roller coaster cart passes through the clothoid loop one experiences acceleration based on two main factors. A rightward moving roller coaster car gradually becomes an upward moving roller coaster car and a leftward moving roller coaster car then a downward moving roller coaster car. Roller coasters are almost entirely driven by different forces of inertia gravity and centripetal.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Gravity plays a huge part in roller coaster physics. The physics of a roller coaster also involves work energy friction inertia and air resistance. As the roller coaster cart passes through the clothoid loop one experiences acceleration based on two main factors. In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track. A roller coaster usually begins with a mechanical device such as a chain and motor which exerts a force on the car trains to lift them to the top of the hill.
 Source: uwgb.edu
Source: uwgb.edu
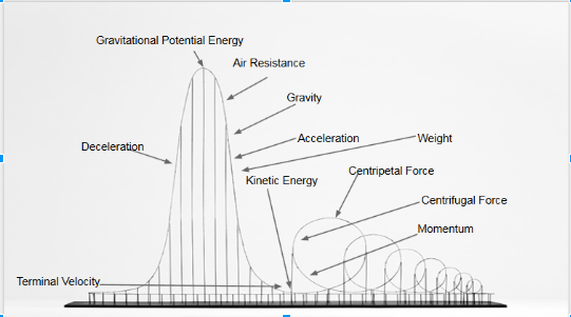
The basic principles of roller coaster mechanics have been known since 1865 and since then. The forces experienced by the rider are constantly changing leading to feelings of joy in some riders and nausea in others. The combination of gravity and inertia along with g forces and centripetal acceleration give the body certain sensations as the coaster moves up down and around the track. The constant change in direction and the constant change in speed. In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track.
 Source: worldsciencefestival.com
Source: worldsciencefestival.com
The forces experienced by the rider are constantly changing leading to feelings of joy in some riders and nausea in others. Roller coasters are almost entirely driven by different forces of inertia gravity and centripetal. The purpose of the coaster s initial ascent is to build up a sort of reservoir of potential energy. A roller coaster is a machine that uses gravity and inertia to send a train of cars along a winding track. In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track.
 Source: uwgb.edu
Source: uwgb.edu
A roller coaster usually begins with a mechanical device such as a chain and motor which exerts a force on the car trains to lift them to the top of the hill. The purpose of the coaster s initial ascent is to build up a sort of reservoir of potential energy. As the roller coaster cart passes through the clothoid loop one experiences acceleration based on two main factors. The forces experienced by the rider are constantly changing leading to feelings of joy in some riders and nausea in others. The basic principles of roller coaster mechanics have been known since 1865 and since then.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The basic principles of roller coaster mechanics have been known since 1865 and since then. In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track. The constant change in direction and the constant change in speed. A roller coaster is a machine that uses gravity and inertia to send a train of cars along a winding track. As a coaster gets higher gravity can pull the cars down faster and faster to push them along the tracks.

The physics of a roller coaster also involves work energy friction inertia and air resistance. As a coaster gets higher gravity can pull the cars down faster and faster to push them along the tracks. A roller coaster is a machine that uses gravity and inertia to send a train of cars along a winding track. The forces experienced by the rider are constantly changing leading to feelings of joy in some riders and nausea in others. In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track.
Source: physics.stackexchange.com
As a coaster gets higher gravity can pull the cars down faster and faster to push them along the tracks. A roller coaster usually begins with a mechanical device such as a chain and motor which exerts a force on the car trains to lift them to the top of the hill. The combination of gravity and inertia along with g forces and centripetal acceleration give the body certain sensations as the coaster moves up down and around the track. As a coaster gets higher gravity can pull the cars down faster and faster to push them along the tracks. The constant change in direction and the constant change in speed.
 Source: hk-phy.org
Source: hk-phy.org
A rightward moving roller coaster car gradually becomes an upward moving roller coaster car and a leftward moving roller coaster car then a downward moving roller coaster car. A roller coaster usually begins with a mechanical device such as a chain and motor which exerts a force on the car trains to lift them to the top of the hill. The combination of gravity and inertia along with g forces and centripetal acceleration give the body certain sensations as the coaster moves up down and around the track. Return to amusement park physics page. A roller coaster is a machine that uses gravity and inertia to send a train of cars along a winding track.
 Source: rollercoasterphysicssd.weebly.com
Source: rollercoasterphysicssd.weebly.com
As the roller coaster cart passes through the clothoid loop one experiences acceleration based on two main factors. A rightward moving roller coaster car gradually becomes an upward moving roller coaster car and a leftward moving roller coaster car then a downward moving roller coaster car. Return to amusement park physics page. The constant change in direction and the constant change in speed. Roller coasters are almost entirely driven by different forces of inertia gravity and centripetal.
 Source: worldsciencefestival.com
Source: worldsciencefestival.com
The forces experienced by the rider are constantly changing leading to feelings of joy in some riders and nausea in others. A roller coaster is a machine that uses gravity and inertia to send a train of cars along a winding track. The basic principles of roller coaster mechanics have been known since 1865 and since then. In summary the physics of roller coasters in general is a combination of gravitational potential energy converted into kinetic energy high speed and using this speed to create centripetal acceleration around different portions of the track. The physics of a roller coaster also involves work energy friction inertia and air resistance.
 Source: sites.google.com
Source: sites.google.com
As a coaster gets higher gravity can pull the cars down faster and faster to push them along the tracks. The constant change in direction and the constant change in speed. The forces experienced by the rider are constantly changing leading to feelings of joy in some riders and nausea in others. The basic principles of roller coaster mechanics have been known since 1865 and since then. Roller coasters are almost entirely driven by different forces of inertia gravity and centripetal.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
As the roller coaster cart passes through the clothoid loop one experiences acceleration based on two main factors. The constant change in direction and the constant change in speed. The basic principles of roller coaster mechanics have been known since 1865 and since then. The forces experienced by the rider are constantly changing leading to feelings of joy in some riders and nausea in others. A rightward moving roller coaster car gradually becomes an upward moving roller coaster car and a leftward moving roller coaster car then a downward moving roller coaster car.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title roller coaster physics by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.