Sensory receptors in skin
Sensory Receptors In Skin. Physiologically the beginning of the sensory process. The sensory receptors in the skin are. The types of sensory receptors according to location include cutaneous receptors and mechanoreceptors. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors respond to pressure sensations on the skin and include merkel s corpuscles meissner s corpuscles and bulboid corpuscles.
 Receptors In Skin Skin Has Three Separate Layers Ppt Video Online Download From slideplayer.com
Receptors In Skin Skin Has Three Separate Layers Ppt Video Online Download From slideplayer.com
Cutaneous mechanoreceptors respond to pressure sensations on the skin and include merkel s corpuscles meissner s corpuscles and bulboid corpuscles. The receiver receives information from the stimulus and initiates a process of. Free nerve endings characterize the nociceptors and thermoreceptors. An exteroceptor is a receptor that is located near a stimulus in the external environment such as the somatosensory receptors that are located in the skin. Merkel s disks meissner s corpuscles ruffini s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles. Other receptors are located inside the body such as the baroceptors in the blood vessels.
Mechanoreceptors on the other hand are located in muscle spindles enabling them to detect muscle stretch.
They detect pressure temperature and vibrations on or around the skin. These include nociceptors and thermoreceptors. Mechanoreceptors on the other hand are located in muscle spindles enabling them to detect muscle stretch. An interoceptor is one that interprets stimuli from internal organs and tissues such as the receptors that sense the increase in blood pressure in the aorta or carotid sinus. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors respond to pressure sensations on the skin and include merkel s corpuscles meissner s corpuscles and bulboid corpuscles. These receptors perceive sensations such as pressure vibrations and texture.
 Source: 123rf.com
Source: 123rf.com
Mechanoreceptors on the other hand are located in muscle spindles enabling them to detect muscle stretch. They detect pressure temperature and vibrations on or around the skin. The sensory receptors in the skin such as meissner s and pacinian corpuscles as well as free nerve endings are classified as general sensory receptors. These receptors are very good at sensing the continuous pressure of an object touching or indenting the skin but are not very good at sensing when the stimulus started or ended. Encapsulated receptors consist of the remaining types of cutaneous receptors.
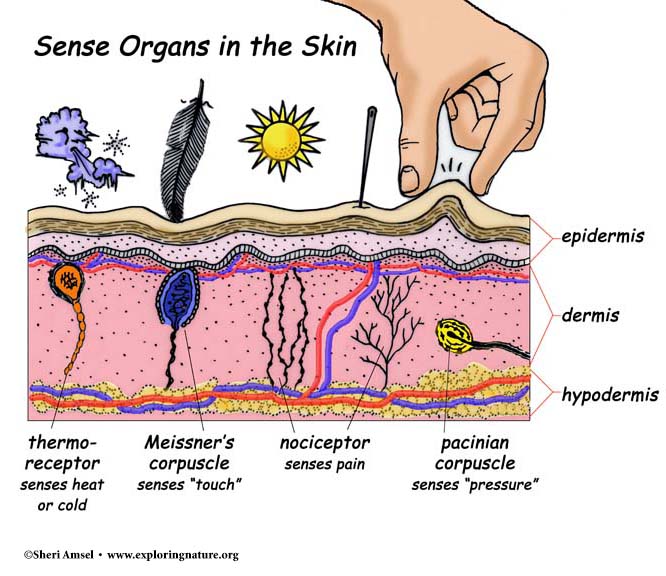 Source: exploringnature.org
Source: exploringnature.org
The sensory receptors in the skin are. The sensory receptors in the skin such as meissner s and pacinian corpuscles as well as free nerve endings are classified as general sensory receptors. The sensory receptors they are highly specialized structures found in the sensory organs eyes ears tongue nose and skin and are responsible for receiving the stimuli that reach the body. 3 4 kg and 20 square feet in an adult is a giant washable stretchable tough water proof sensory apparatus covering your whole body. Encapsulation exists for specialized functioning.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Encapsulated receptors consist of the remaining types of cutaneous receptors. These include nociceptors and thermoreceptors. An interoceptor is one that interprets stimuli from internal organs and tissues such as the receptors that sense the increase in blood pressure in the aorta or carotid sinus. The types of sensory receptors according to location include cutaneous receptors and mechanoreceptors. These receptors perceive sensations such as pressure vibrations and texture.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Somatic sensory receptors near the surface of the skin can usually be divided into two groups based on morphology. Somatic sensory receptors near the surface of the skin can usually be divided into two groups based on morphology. The dermis is the inside layer of skin. These include nociceptors and thermoreceptors. The sensory receptors in the skin are.
 Source: neurones.co.uk
Source: neurones.co.uk
Mechanoreceptors on the other hand are located in muscle spindles enabling them to detect muscle stretch. Somatic sensory receptors near the surface of the skin can usually be divided into two groups based on morphology. These receptors include bare nerve endings nociception thermal sensation and encapsulated endings. They detect pressure temperature and vibrations on or around the skin. Encapsulation exists for specialized functioning.
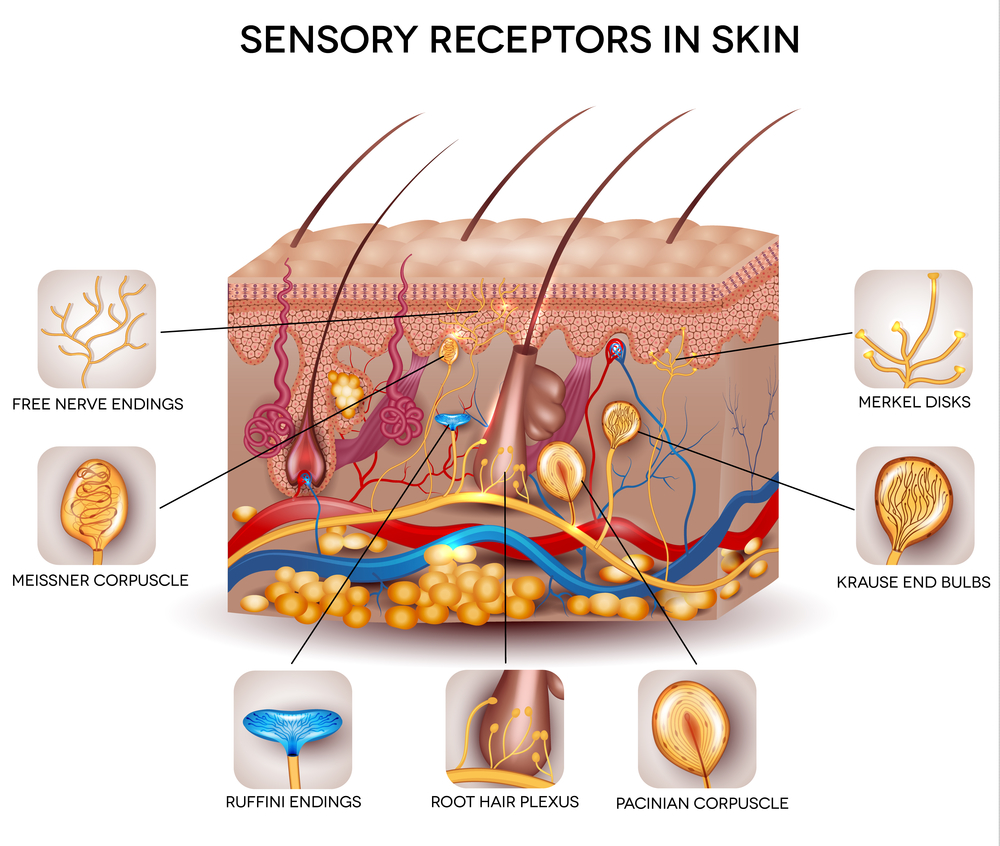 Source: integrativelearningcenter.org
Source: integrativelearningcenter.org
An interoceptor is one that interprets stimuli from internal organs and tissues such as the receptors that sense the increase in blood pressure in the aorta or carotid sinus. There are four known types of mechanoreceptors whose only function is to perceive indentions and vibrations of the skin. These receptors are very good at sensing the continuous pressure of an object touching or indenting the skin but are not very good at sensing when the stimulus started or ended. Glabrous skin and hairy skin contain a wide variety of sensory receptors for detecting mechanical thermal or nociceptive consciously perceived as painful stimuli applied on the body surface. Anatomically a sensory receptor is the end of a sensory nerve.
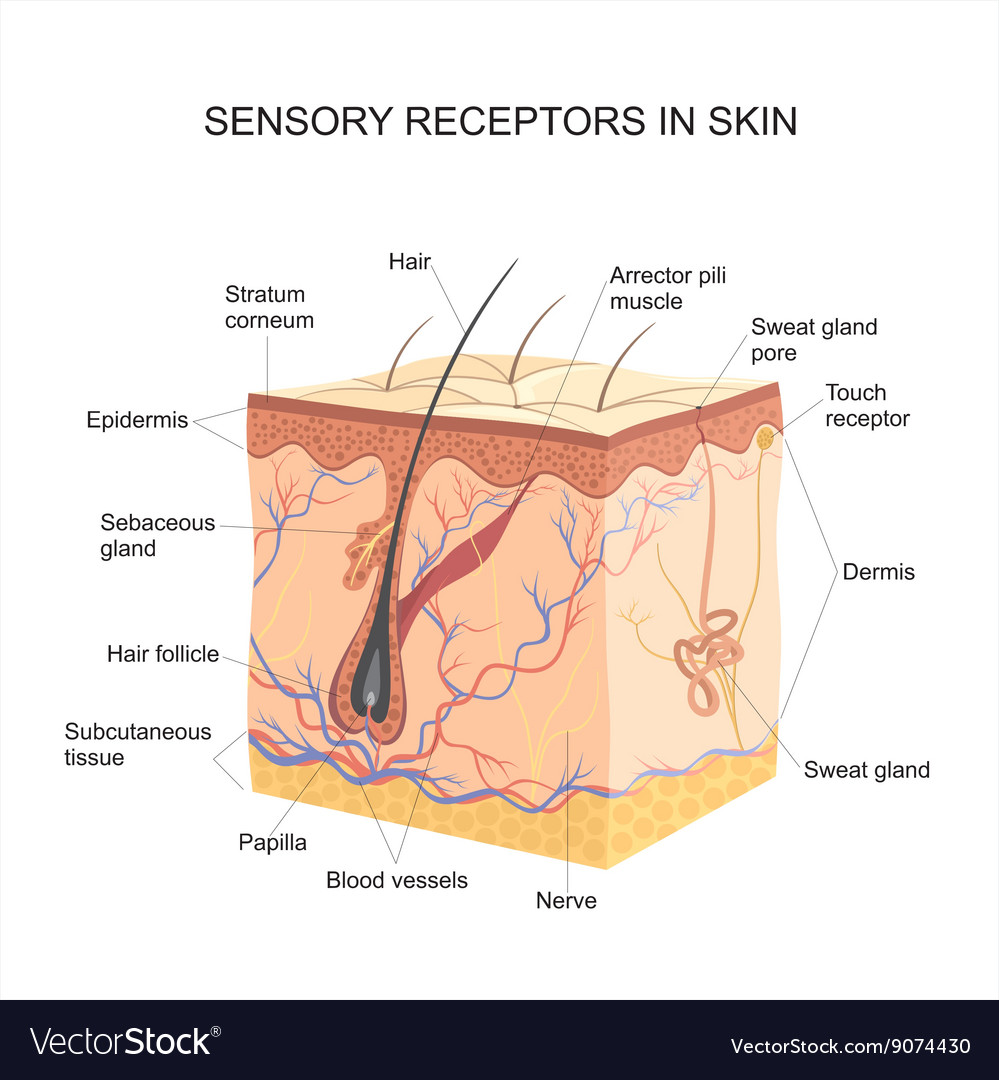 Source: vectorstock.com
Source: vectorstock.com
Somatic sensory receptors near the surface of the skin can usually be divided into two groups based on morphology. These include nociceptors and thermoreceptors. The types of sensory receptors according to location include cutaneous receptors and mechanoreceptors. These receptors include bare nerve endings nociception thermal sensation and encapsulated endings. Sensory receptors located in the dermis or epidermis of the skin are called cutaneous receptors.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Receptors that detect temperature are made up of free nerve endings on the skin and are called thermoreceptors. Skin receptors also called cutaneous receptors are part of the somatosensory system. Merkel s disks meissner s corpuscles ruffini s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles. Other receptors are located inside the body such as the baroceptors in the blood vessels. Encapsulation exists for specialized functioning.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
These receptors are very good at sensing the continuous pressure of an object touching or indenting the skin but are not very good at sensing when the stimulus started or ended. These receptors include bare nerve endings nociception thermal sensation and encapsulated endings. The skin all 6 10 lb. Merkel s disks meissner s corpuscles ruffini s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles. Sensory receptors located in the dermis or epidermis of the skin are called cutaneous receptors.
 Source: biologyboom.com
Source: biologyboom.com
These receptors include bare nerve endings nociception thermal sensation and encapsulated endings. Receptors that detect temperature are made up of free nerve endings on the skin and are called thermoreceptors. Free nerve endings characterize the nociceptors and thermoreceptors. These receptors are very good at sensing the continuous pressure of an object touching or indenting the skin but are not very good at sensing when the stimulus started or ended. The epidermis is the outside layer of your skin.
 Source: macrovector.com
Source: macrovector.com
Encapsulation exists for specialized functioning. The sensory receptors in the skin such as meissner s and pacinian corpuscles as well as free nerve endings are classified as general sensory receptors. Sensory receptors located in the dermis or epidermis of the skin are called cutaneous receptors. Encapsulation exists for specialized functioning. These include nociceptors and thermoreceptors.
 Source: shutterstock.com
Source: shutterstock.com
Somatic sensory receptors near the surface of the skin can usually be divided into two groups based on morphology. There are four known types of mechanoreceptors whose only function is to perceive indentions and vibrations of the skin. Other receptors are located inside the body such as the baroceptors in the blood vessels. These receptors perceive sensations such as pressure vibrations and texture. Anatomically a sensory receptor is the end of a sensory nerve.
 Source: grants.hhp.uh.edu
Source: grants.hhp.uh.edu
These receptors perceive sensations such as pressure vibrations and texture. The skin all 6 10 lb. Ruffini s end organ skin stretch end bulbs of krause cold meissner s corpuscle changes in texture slow vibrations pacinian corpuscle deep pressure fast vibrations merkel s disc sustained touch and pressure free nerve endings. These receptors include bare nerve endings nociception thermal sensation and encapsulated endings. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors respond to pressure sensations on the skin and include merkel s corpuscles meissner s corpuscles and bulboid corpuscles.
 Source: blogs.aalto.fi
Source: blogs.aalto.fi
Free nerve endings characterize the nociceptors and thermoreceptors. Merkel s disks meissner s corpuscles ruffini s corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles. The dermis is the inside layer of skin. There are four known types of mechanoreceptors whose only function is to perceive indentions and vibrations of the skin. Physiologically the beginning of the sensory process.
 Source: srigspeaks.com
Source: srigspeaks.com
The receiver receives information from the stimulus and initiates a process of. Physiologically the beginning of the sensory process. Other members of this group of receptors include free nerve endings in the connective tissue as well as the muscle spindle and golgi tendon organ found in the musculoskeletal system. The receiver receives information from the stimulus and initiates a process of. They detect pressure temperature and vibrations on or around the skin.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title sensory receptors in skin by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






