Structure of bread mould
Structure Of Bread Mould. They can be found on any surface and in any condition. It is one of the most common fungi in the world and has a global distribution although it is most commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions. It is a member of zygomycota and considered the most important species in the genus rhizopus. Zygospores figure 2 and zygospore illustration do not occur inside any kind of enclosing structure but are produced by the direct fusion of two hyphal protrusions suspensors from neighbouring filaments.
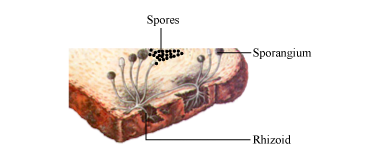 Describe The Structure Of Bread Mould Biology 10906131 Meritnation Com From meritnation.com
Describe The Structure Of Bread Mould Biology 10906131 Meritnation Com From meritnation.com
They appear on the surface of bread that may be left open in normal conditions say on the kitchen countertop. Bread mold fungus is a member of the zygomycota. The hyphae are generally transparent so the mycelium appe. To study the growth of mold on bread samples every alternate day for a course of 2 weeks. This is many times studied in school with a simple experiment. They can be found on any surface and in any condition.
A mold or mould is a fungus that grows in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae.
Mushrooms and toadstools are a type of fungi. Growth of bread mold. It appears on the bread surface as a windblown spore. Mushrooms and toadstools are a type of fungi. It is a common agent of decomposition of stored foods. Bread mold is a type of fungus and is therefore eukaryotic contains membrane bound organelles and multi cellular.
 Source: meritnation.com
Source: meritnation.com
It is a common agent of decomposition of stored foods. Bread mold is a type of fungus and is therefore eukaryotic contains membrane bound organelles and multi cellular. It is a member of zygomycota and considered the most important species in the genus rhizopus. The network of these tubular branching hyphae called a mycelium is considered a single organism. You can see a diagram of this sexual stage in the zygomycota section of our kinds of fungus page.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Rhizopus stolonifer is commonly known as black bread mold. Microscopic parts of the bread mold fungi known as spores are present in the air all around us. Bread mold is a type of fungus and is therefore eukaryotic contains membrane bound organelles and multi cellular. In contrast fungi that can adopt a single celled growth habit are called yeasts. You can see a diagram of this sexual stage in the zygomycota section of our kinds of fungus page.

They appear on the surface of bread that may be left open in normal conditions say on the kitchen countertop. The network of these tubular branching hyphae called a mycelium is considered a single organism. Bread mold project aim. Molds are a large and taxonomically diverse number of fungal species in which the growth of hyphae results in discoloration and a fuzzy appearance especially on food. They can be found on any surface and in any condition.
 Source: kenyaplex.com
Source: kenyaplex.com
You can see a diagram of this sexual stage in the zygomycota section of our kinds of fungus page. You can see a diagram of this sexual stage in the zygomycota section of our kinds of fungus page. Zygospores figure 2 and zygospore illustration do not occur inside any kind of enclosing structure but are produced by the direct fusion of two hyphal protrusions suspensors from neighbouring filaments. Usually zygospores are recognized as large nearly spherical often dark brown or black rough walled spores with two connecting hyphae representing the two mating gametangia figure 2c. Molds are a large and taxonomically diverse number of fungal species in which the growth of hyphae results in discoloration and a fuzzy appearance especially on food.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Growth of bread mold. Zygospores figure 2 and zygospore illustration do not occur inside any kind of enclosing structure but are produced by the direct fusion of two hyphal protrusions suspensors from neighbouring filaments. With adequate moisture and nutrients from the bread this spore sprouts and grows hair like structures. It appears on the bread surface as a windblown spore. Mushrooms and toadstools are a type of fungi.
 Source: biologywise.com
Source: biologywise.com
Mold grows on food and other organic matter and thus breaks it down into slime by which it extracts nutrient for its growth. Bread mold project aim. Mold grows on food and other organic matter and thus breaks it down into slime by which it extracts nutrient for its growth. Molds are a large and taxonomically diverse number of fungal species in which the growth of hyphae results in discoloration and a fuzzy appearance especially on food. It appears on the bread surface as a windblown spore.
 Source: backyardnature.net
Source: backyardnature.net
Growth of bread mold. Mushrooms and toadstools are a type of fungi. It appears on the bread surface as a windblown spore. Mold cells are present in a long filamentous structure called a hypha. Bread mold fungus is a member of the zygomycota.
 Source: classnotes.org.in
Source: classnotes.org.in
The mold cells are connected via pores in the septa between cells and are surrounded by a tube shaped cell wall. The mold cells are connected via pores in the septa between cells and are surrounded by a tube shaped cell wall. The hyphae are generally transparent so the mycelium appe. Bread mold project aim. Molds are a large and taxonomically diverse number of fungal species in which the growth of hyphae results in discoloration and a fuzzy appearance especially on food.
 Source: kenyaplex.com
Source: kenyaplex.com
Mold cells are present in a long filamentous structure called a hypha. Growth of bread mold. The hyphae are generally transparent so the mycelium appe. Members of the zygomycota under certain conditions the hyphae which come in positive and negative mating strains come together and form sexual structures. Microscopic parts of the bread mold fungi known as spores are present in the air all around us.
 Source: meritnation.com
Source: meritnation.com
Bread mold fungus is a member of the zygomycota. It is one of the most common fungi in the world and has a global distribution although it is most commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions. With adequate moisture and nutrients from the bread this spore sprouts and grows hair like structures. Bread mold fungus is a member of the zygomycota. Growth of bread mold.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
They appear on the surface of bread that may be left open in normal conditions say on the kitchen countertop. Microscopic parts of the bread mold fungi known as spores are present in the air all around us. Bread mold is a type of fungus and is therefore eukaryotic contains membrane bound organelles and multi cellular. With adequate moisture and nutrients from the bread this spore sprouts and grows hair like structures. Bread mold project aim.
 Source: domainsoflife.yolasite.com
Source: domainsoflife.yolasite.com
Usually zygospores are recognized as large nearly spherical often dark brown or black rough walled spores with two connecting hyphae representing the two mating gametangia figure 2c. You can see a diagram of this sexual stage in the zygomycota section of our kinds of fungus page. Usually zygospores are recognized as large nearly spherical often dark brown or black rough walled spores with two connecting hyphae representing the two mating gametangia figure 2c. Mold cells are present in a long filamentous structure called a hypha. They can be found on any surface and in any condition.
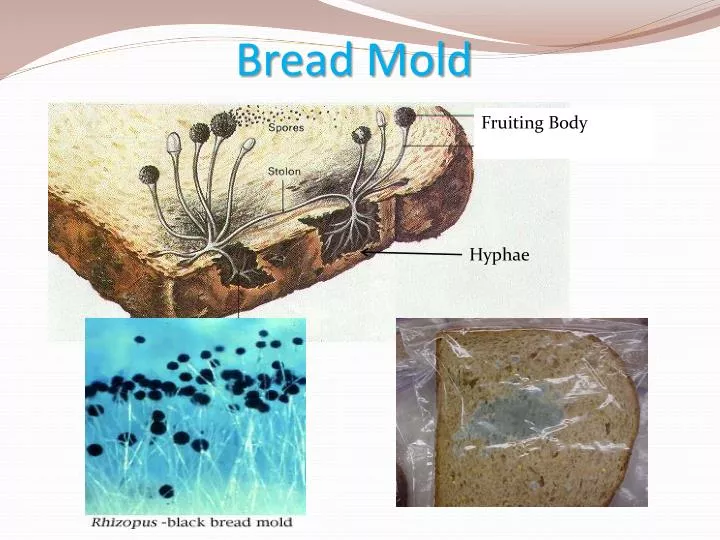 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Bread mold has a very simple lifecycle. It is a common agent of decomposition of stored foods. This is many times studied in school with a simple experiment. Bread mold has a very simple lifecycle. Bread mold project aim.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
Mold grows on food and other organic matter and thus breaks it down into slime by which it extracts nutrient for its growth. It is a member of zygomycota and considered the most important species in the genus rhizopus. To study the growth of mold on bread samples every alternate day for a course of 2 weeks. Bread mold fungus is a member of the zygomycota. Growth of bread mold.
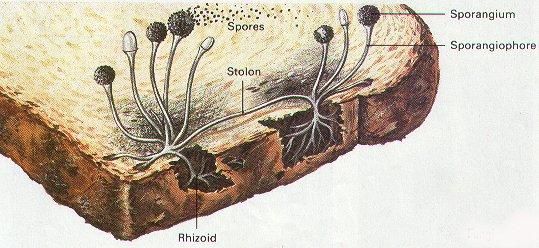 Source: flipscience.ph
Source: flipscience.ph
Members of the zygomycota under certain conditions the hyphae which come in positive and negative mating strains come together and form sexual structures. The hyphae are generally transparent so the mycelium appe. Mushrooms and toadstools are a type of fungi. You can see a diagram of this sexual stage in the zygomycota section of our kinds of fungus page. The mold cells are connected via pores in the septa between cells and are surrounded by a tube shaped cell wall.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title structure of bread mould by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







