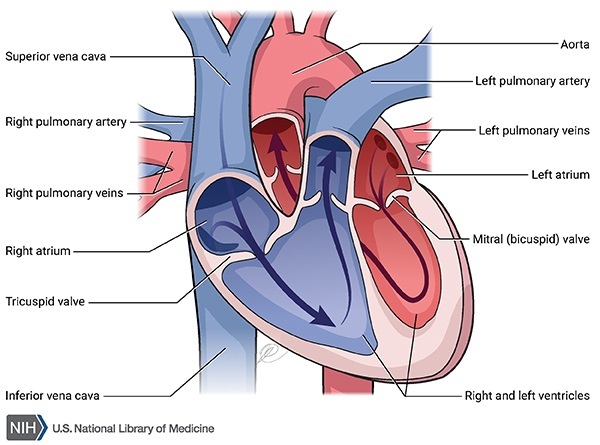
To what structures do the pulmonary arteries lead
To What Structures Do The Pulmonary Arteries Lead. The now oxygen rich blood travels through lung capillaries to. It connects to the left lung and branches into smaller vessels within the lung. The pulmonary artery leaves the right ventricle divides and sends one branch to each lung. Pulmonary arteries lead from the heart to the lungs.
 Pulmonary Arteries And Veins Anatomy And Function Kenhub From kenhub.com
Pulmonary Arteries And Veins Anatomy And Function Kenhub From kenhub.com
The left and right pulmonary arteries which act to deliver. In the developed heart the pulmonary trunk pulmonary artery or main pulmonary artery begins at the base of the right ventricle. Robert lewis maynard noel downes in anatomy and histology of the laboratory rat in toxicology and biomedical research 2019. Directs blood to the left lung. The nasopharynx oropharynx and related structures often are called the upper airway figure 34 2. The pulmonary arteries function to deliver blood to the lungs to acquire oxygen.
The pulmonary arteries are part of the pulmonary circulation which also includes pulmonary veins and pulmonary capillaries.
In the developed heart the pulmonary trunk pulmonary artery or main pulmonary artery begins at the base of the right ventricle. Left pulmonary artery the main pulmonary artery is responsible for transporting oxygen depleted blood away from the heart and back toward the lungs. It then would pass through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle. There is also less of them. These structures are lined with a ciliated mucosa with a very rich vascular supply. Left pulmonary artery lpa.
 Source: medlineplus.gov
Source: medlineplus.gov
Left pulmonary artery the main pulmonary artery is responsible for transporting oxygen depleted blood away from the heart and back toward the lungs. The pulmonary arteries function to deliver blood to the lungs to acquire oxygen. It then would pass through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle. In the process of respiration oxygen diffuses across capillary vessels in lung alveoli and attach to red blood cells in the blood. The nasopharynx oropharynx and related structures often are called the upper airway figure 34 2.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
The nasopharynx oropharynx and related structures often are called the upper airway figure 34 2. The purpose of the pulmonary circulation is to transfer oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood in the body and the air that s inhaled and exhaled in the lungs. In the developed heart the pulmonary trunk pulmonary artery or main pulmonary artery begins at the base of the right ventricle. Directs blood to the left lung. Robert lewis maynard noel downes in anatomy and histology of the laboratory rat in toxicology and biomedical research 2019.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
From there it would pass through the pulmonary valve and go through the pulmonary arteries and into the lungs. The pulmonary trunk is a short and stout wide structure that is about 5 cm in length and 3 cm in diameter which branches into 2 pulmonary arteries. In the developed heart the pulmonary trunk pulmonary artery or main pulmonary artery begins at the base of the right ventricle. The pulmonary arteries function to deliver blood to the lungs to acquire oxygen. The pulmonary artery leaves the right ventricle divides and sends one branch to each lung.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
The pulmonary artery leaves the right ventricle divides and sends one branch to each lung. It connects to the left lung and branches into smaller vessels within the lung. Consequently the pulmonary arteries are usually slightly smaller and thinner. In the foetus the pulmonary circulation is a high pressure system and in man the foetal pulmonary artery is not very different in structure from the foetal aorta. It is shorter than the rpa and is a direct extension of the pulmonary trunk.
 Source: verywellhealth.com
Source: verywellhealth.com
The nasopharynx oropharynx and related structures often are called the upper airway figure 34 2. Left pulmonary artery the main pulmonary artery is responsible for transporting oxygen depleted blood away from the heart and back toward the lungs. Systemic arteries go everywhere else. These structures are lined with a ciliated mucosa with a very rich vascular supply. In the process of respiration oxygen diffuses across capillary vessels in lung alveoli and attach to red blood cells in the blood.
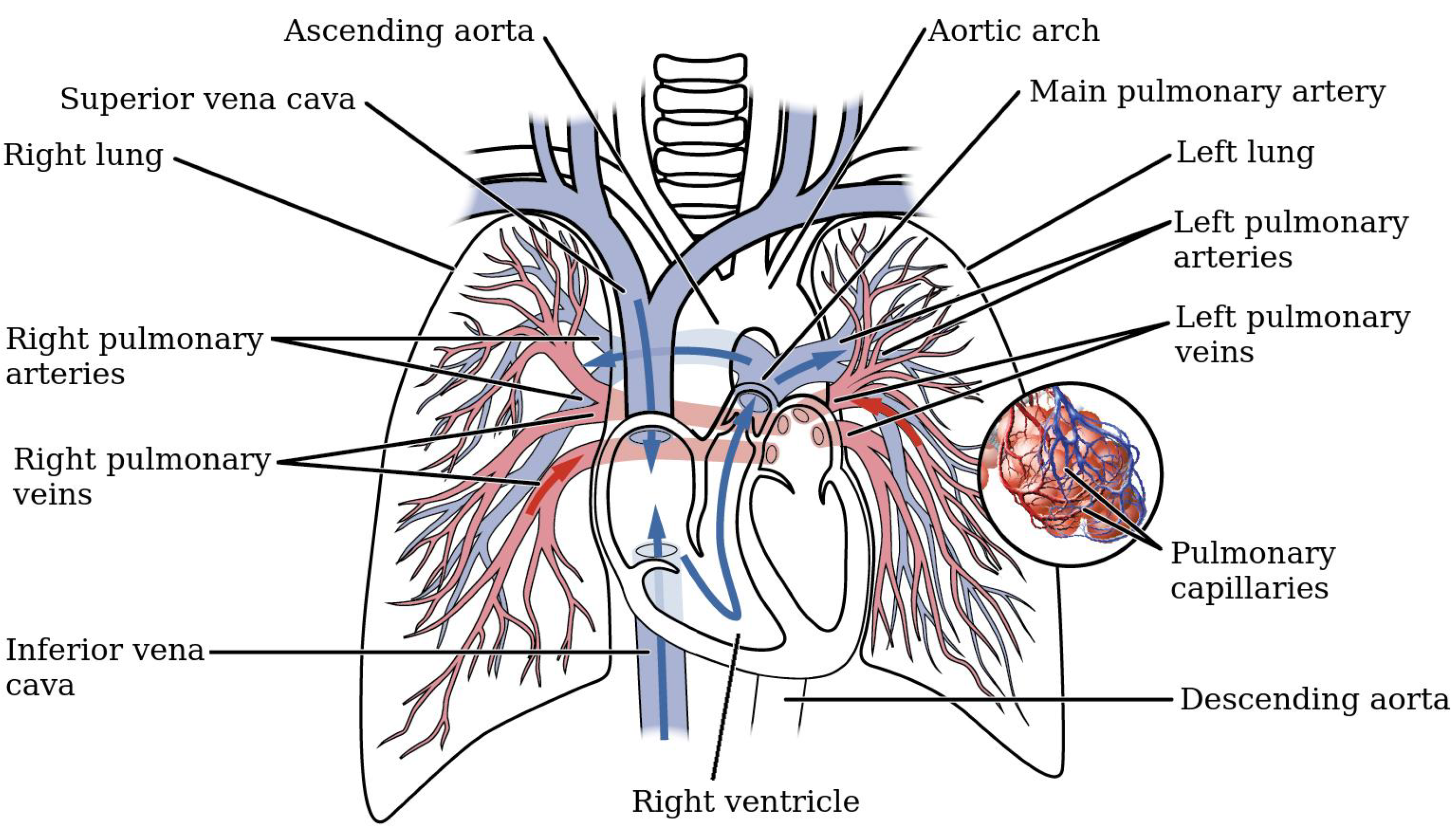 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs the largest pulmonary artery is the main pulmonary artery or pulmonary trunk from the heart and the smallest ones are the arterioles which lead to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli. It then would pass through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle. The now oxygen rich blood travels through lung capillaries to. It connects to the left lung and branches into smaller vessels within the lung. It is shorter than the rpa and is a direct extension of the pulmonary trunk.
 Source: kenhub.com
Source: kenhub.com
The purpose of the pulmonary circulation is to transfer oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood in the body and the air that s inhaled and exhaled in the lungs. The now oxygen rich blood travels through lung capillaries to. It is shorter than the rpa and is a direct extension of the pulmonary trunk. Systemic arteries go everywhere else. Left pulmonary artery lpa.
 Source: kenhub.com
Source: kenhub.com
The pulmonary trunk is a short and stout wide structure that is about 5 cm in length and 3 cm in diameter which branches into 2 pulmonary arteries. In the developed heart the pulmonary trunk pulmonary artery or main pulmonary artery begins at the base of the right ventricle. It is shorter than the rpa and is a direct extension of the pulmonary trunk. Robert lewis maynard noel downes in anatomy and histology of the laboratory rat in toxicology and biomedical research 2019. The main artery splits into the left pulmonary.
 Source: kenhub.com
Source: kenhub.com
The nasopharynx oropharynx and related structures often are called the upper airway figure 34 2. Left pulmonary artery the main pulmonary artery is responsible for transporting oxygen depleted blood away from the heart and back toward the lungs. The nasopharynx oropharynx and related structures often are called the upper airway figure 34 2. The mucosal lining warms and humidifies inspired air to 100 and removes foreign particles from it as it passes into the lungs. From there it would pass through the pulmonary valve and go through the pulmonary arteries and into the lungs.
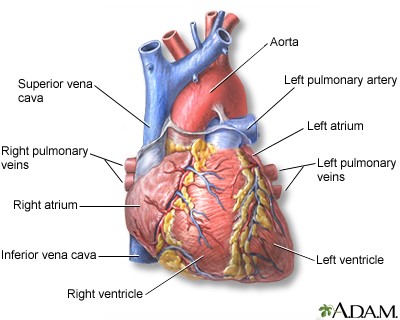 Source: wakehealth.edu
Source: wakehealth.edu
It is shorter than the rpa and is a direct extension of the pulmonary trunk. It connects to the left lung and branches into smaller vessels within the lung. The main artery splits into the left pulmonary. The pulmonary artery leaves the right ventricle divides and sends one branch to each lung. There is also less of them.
 Source: kenhub.com
Source: kenhub.com
In the developed heart the pulmonary trunk pulmonary artery or main pulmonary artery begins at the base of the right ventricle. It is shorter than the rpa and is a direct extension of the pulmonary trunk. Consequently the pulmonary arteries are usually slightly smaller and thinner. The nasopharynx oropharynx and related structures often are called the upper airway figure 34 2. Pulmonary arteries lead from the heart to the lungs.
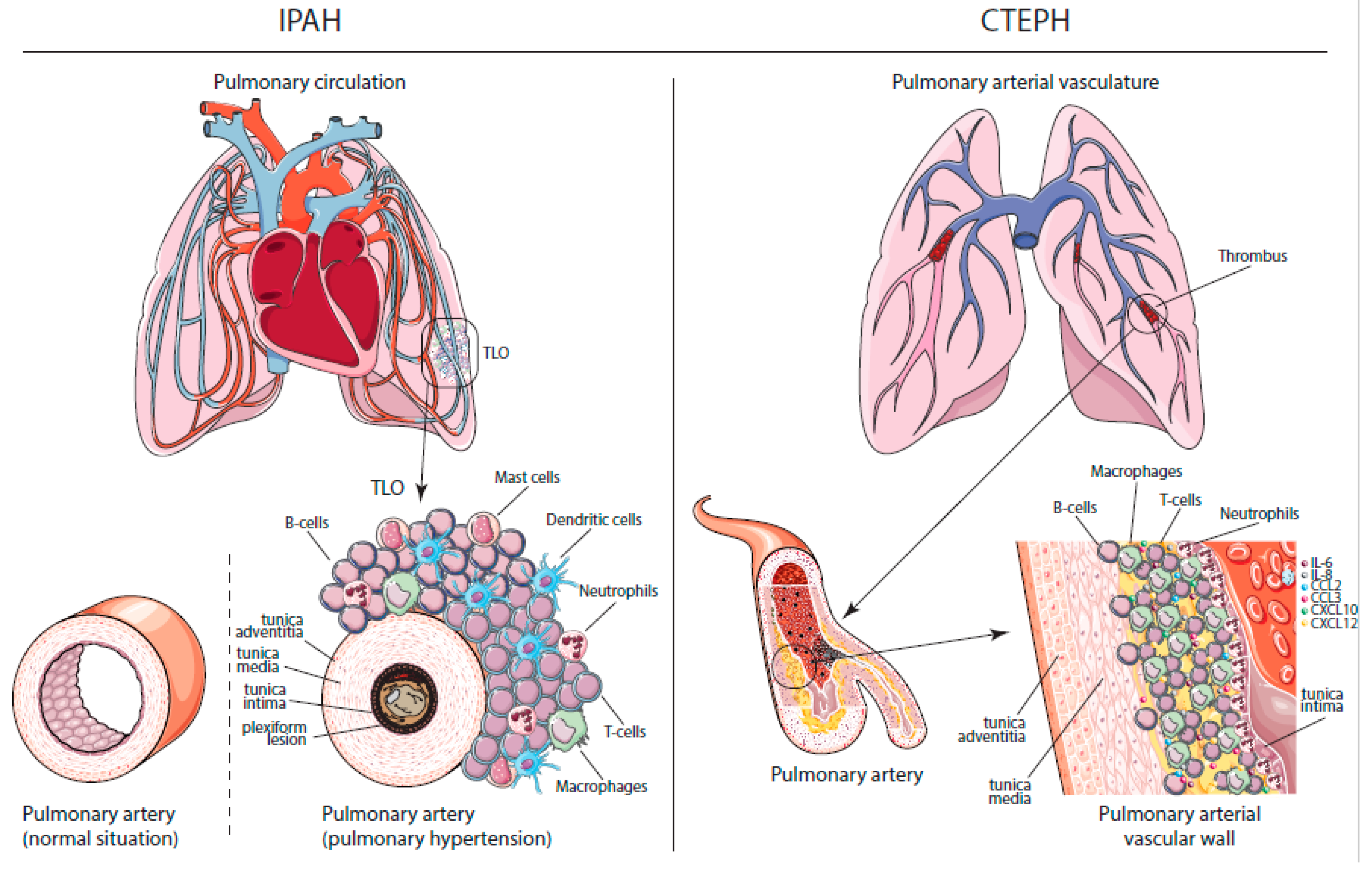 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
From there it would pass through the pulmonary valve and go through the pulmonary arteries and into the lungs. The now oxygen rich blood travels through lung capillaries to. The nasopharynx oropharynx and related structures often are called the upper airway figure 34 2. Left pulmonary artery the main pulmonary artery is responsible for transporting oxygen depleted blood away from the heart and back toward the lungs. Pulmonary arteries lead from the heart to the lungs.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Left pulmonary artery the main pulmonary artery is responsible for transporting oxygen depleted blood away from the heart and back toward the lungs. The now oxygen rich blood travels through lung capillaries to. The pulmonary artery leaves the right ventricle divides and sends one branch to each lung. Consequently the pulmonary arteries are usually slightly smaller and thinner. In the process of respiration oxygen diffuses across capillary vessels in lung alveoli and attach to red blood cells in the blood.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
In the foetus the pulmonary circulation is a high pressure system and in man the foetal pulmonary artery is not very different in structure from the foetal aorta. The left and right pulmonary arteries which act to deliver. These structures are lined with a ciliated mucosa with a very rich vascular supply. Consequently the pulmonary arteries are usually slightly smaller and thinner. The pulmonary arteries are part of the pulmonary circulation which also includes pulmonary veins and pulmonary capillaries.
 Source: achaheart.org
Source: achaheart.org
Pulmonary arteries lead from the heart to the lungs. The main artery splits into the left pulmonary. The left and right pulmonary arteries which act to deliver. It is shorter than the rpa and is a direct extension of the pulmonary trunk. It then would pass through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title to what structures do the pulmonary arteries lead by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.