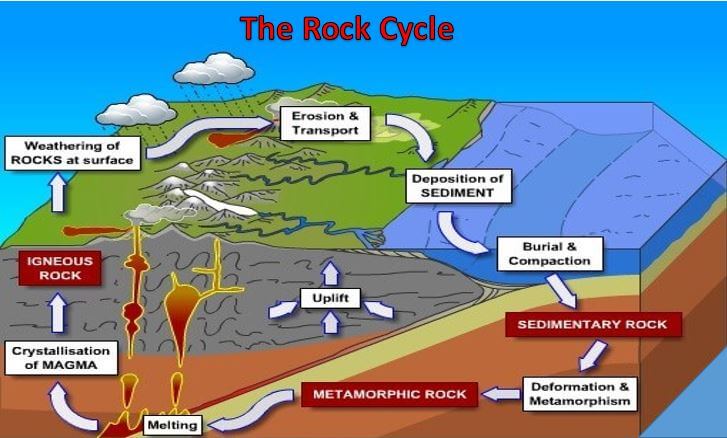
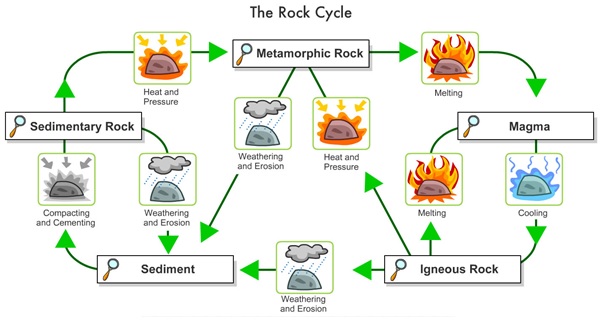
What is heat and pressure in the rock cycle
What Is Heat And Pressure In The Rock Cycle. During sedimentation the sediments are laid down or deposited. Over a very long period of time sedimentary and igneous rocks end up being buried deep underground the soil usually because of the movement of tectonic plates. The rock cycle explains how rocks and natural processes are related melting weathering pressure heat sedimentary metamorphic igneous. In order to form a sedimentary rock the accumulated sediment must become compacted and cemented together.
 The Rock Cycle From gsi.ie
The Rock Cycle From gsi.ie
The atoms in rocks rearrange to form bigger and heavier minerals. During sedimentation the sediments are laid down or deposited. When a rock is exposed to extreme heat and pressure within the earth but does not melt the rock becomes metamorphosed. The heat and pressure is the compacting of the sediments and all other rocks to melt and form magma or become metamorphic rock which hardens into an igneous rock which breaks into sediments and so. The combination of heat and pressure may cause the minerals in the rock to split into layers. Metamorphic rocks are rocks that have been changed from their original form by immense heat or pressure.
Metamorphic rocks begin changing at temperatures of 100 degrees celsius to 800 degrees celsius.
Metamorphic rocks are rocks that have been changed from their original form by immense heat or pressure. A sequence of events involving the formation alteration destruction and reformation. Foliation is the aligning of elongated or platy minerals like hornblende or mica perpendicular to the direction of pressure that is applied. Heat can come from the compressive force of gravity friction between tectonic plates or radioactivity. Pressure builds as rock is buried and more rock piles on top of it. Metamorphic rocks begin changing at temperatures of 100 degrees celsius to 800 degrees celsius.
 Source: sites.google.com
Source: sites.google.com
The combination of heat and pressure may cause the minerals in the rock to split into layers. Heat can come from the compressive force of gravity friction between tectonic plates or radioactivity. Metamorphic rocks have two classes. The rock cycle explains how rocks and natural processes are related melting weathering pressure heat sedimentary metamorphic igneous. When a rock with flat or elongated minerals is put under immense pressure the minerals line up in layers creating foliation.
 Source: gallaghergeologyproject.weebly.com
Source: gallaghergeologyproject.weebly.com
Metamorphic rocks begin changing at temperatures of 100 degrees celsius to 800 degrees celsius. A sequence of events involving the formation alteration destruction and reformation. Heat can come from the compressive force of gravity friction between tectonic plates or radioactivity. The pressure and or heat is so intense that it can transform the basic properties of another type of rock. Foliation is the aligning of elongated or platy minerals like hornblende or mica perpendicular to the direction of pressure that is applied.
 Source: storyboardthat.com
Source: storyboardthat.com
The pressure and or heat is so intense that it can transform the basic properties of another type of rock. In order to form a sedimentary rock the accumulated sediment must become compacted and cemented together. In the rock cycle heat and pressure helps the igneous rock to form a metamorphic rock which forms back into an igneous rock. The combination of heat and pressure may cause the minerals in the rock to split into layers. Foliation is the aligning of elongated or platy minerals like hornblende or mica perpendicular to the direction of pressure that is applied.
 Source: sites.google.com
Source: sites.google.com
When a rock is exposed to extreme heat and pressure within the earth but does not melt the rock becomes metamorphosed. The heat and pressure is the compacting of the sediments and all other rocks to melt and form magma or become metamorphic rock which hardens into an igneous rock which breaks into sediments and so. Heat can come from the compressive force of gravity friction between tectonic plates or radioactivity. The sedimentary rock is helped through heat and pressure to form a. Pressure builds as rock is buried and more rock piles on top of it.
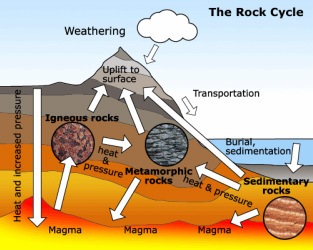
In the rock cycle heat and pressure helps the igneous rock to form a metamorphic rock which forms back into an igneous rock. In order to form a sedimentary rock the accumulated sediment must become compacted and cemented together. The sedimentary rock is helped through heat and pressure to form a. Metamorphic rocks begin changing at temperatures of 100 degrees celsius to 800 degrees celsius. Rocks and debris continue to pile in layers until pressure and heat change the underlying layers to form metamorphic rocks.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
The heat and pressure is the compacting of the sediments and all other rocks to melt and form magma or become metamorphic rock which hardens into an igneous rock which breaks into sediments and so. Heat can come from the compressive force of gravity friction between tectonic plates or radioactivity. Metamorphic rocks are rocks that have been changed from their original form by immense heat or pressure. When a rock is exposed to extreme heat and pressure within the earth but does not melt the rock becomes metamorphosed. Metamorphic rocks begin changing at temperatures of 100 degrees celsius to 800 degrees celsius.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The rock cycle explains how rocks and natural processes are related melting weathering pressure heat sedimentary metamorphic igneous. Metamorphic rocks are rocks that have been changed from their original form by immense heat or pressure. Foliation is the aligning of elongated or platy minerals like hornblende or mica perpendicular to the direction of pressure that is applied. Rock cycle prepared by the michigan department of environmental quality office of geological survey. The rock cycle explains how rocks and natural processes are related melting weathering pressure heat sedimentary metamorphic igneous.
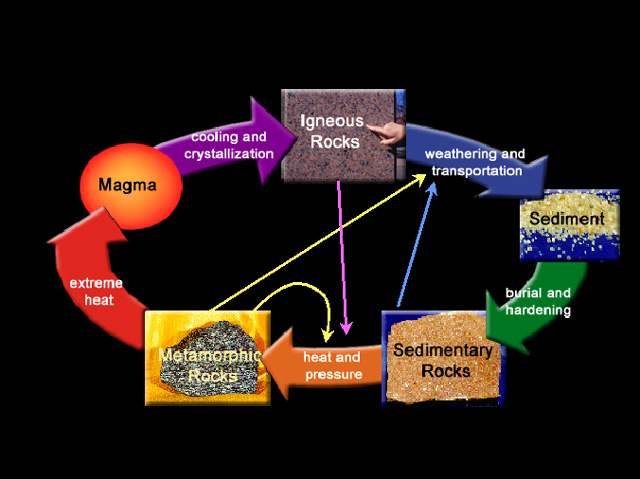 Source: radford.edu
Source: radford.edu
What is the rock cycle. If you squeeze and heat a rock for a few million years it can turn into a new kind of rock. Metamorphic rocks are rocks that have been changed from their original form by immense heat or pressure. Metamorphic rocks begin changing at temperatures of 100 degrees celsius to 800 degrees celsius. Heat can come from the compressive force of gravity friction between tectonic plates or radioactivity.
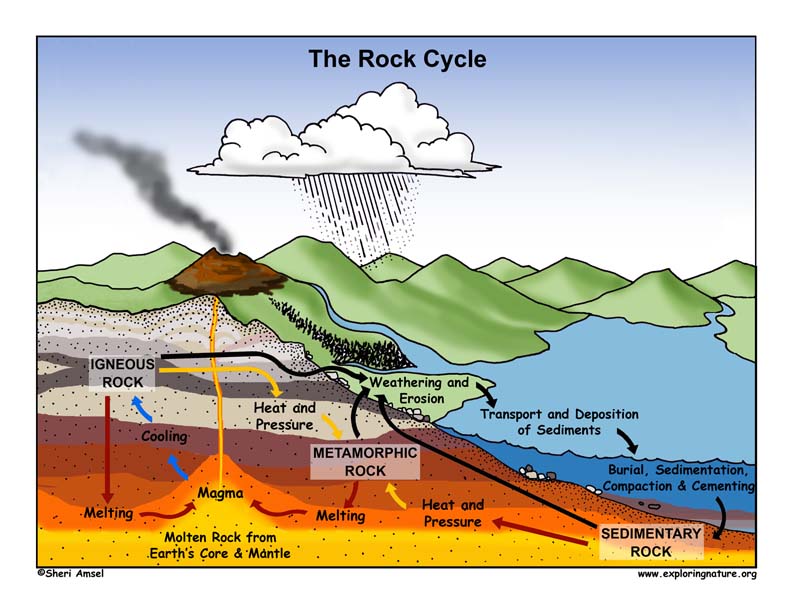 Source: exploringnature.org
Source: exploringnature.org
During sedimentation the sediments are laid down or deposited. Foliation is the aligning of elongated or platy minerals like hornblende or mica perpendicular to the direction of pressure that is applied. Heat can come from the compressive force of gravity friction between tectonic plates or radioactivity. What s more eroded rocks may continue to press and squeeze into sedimentary rocks as the transformations due to pressure and heat take place. Metamorphic rocks are created by intense heat and pressure.
 Source: gsi.ie
Source: gsi.ie
In the rock cycle heat and pressure helps the igneous rock to form a metamorphic rock which forms back into an igneous rock. Deep below the surface these rocks are exposed to high heat and pressure which change them into a different type of rock called metamorphic rock. The heat and pressure is the compacting of the sediments and all other rocks to melt and form magma or become metamorphic rock which hardens into an igneous rock which breaks into sediments and so. Metamorphic rocks are created by intense heat and pressure. Rocks and debris continue to pile in layers until pressure and heat change the underlying layers to form metamorphic rocks.
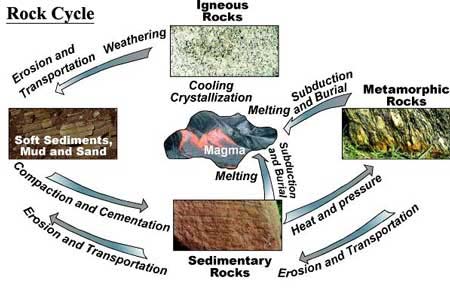 Source: digitalatlas.cose.isu.edu
Source: digitalatlas.cose.isu.edu
The combination of heat and pressure may cause the minerals in the rock to split into layers. During sedimentation the sediments are laid down or deposited. When a rock is exposed to extreme heat and pressure within the earth but does not melt the rock becomes metamorphosed. The sedimentary rock is helped through heat and pressure to form a. When a rock with flat or elongated minerals is put under immense pressure the minerals line up in layers creating foliation.
 Source: brainly.com
Source: brainly.com
Metamorphic rocks are created by intense heat and pressure. What is the rock cycle. Foliation is the aligning of elongated or platy minerals like hornblende or mica perpendicular to the direction of pressure that is applied. Pressure builds as rock is buried and more rock piles on top of it. In order to form a sedimentary rock the accumulated sediment must become compacted and cemented together.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Pressure builds as rock is buried and more rock piles on top of it. In the rock cycle heat and pressure helps the igneous rock to form a metamorphic rock which forms back into an igneous rock. When a rock with flat or elongated minerals is put under immense pressure the minerals line up in layers creating foliation. In order to form a sedimentary rock the accumulated sediment must become compacted and cemented together. Metamorphic rocks begin changing at temperatures of 100 degrees celsius to 800 degrees celsius.
 Source: sfcollege.edu
Source: sfcollege.edu
Foliation is the aligning of elongated or platy minerals like hornblende or mica perpendicular to the direction of pressure that is applied. Heat can come from the compressive force of gravity friction between tectonic plates or radioactivity. When a rock is exposed to extreme heat and pressure within the earth but does not melt the rock becomes metamorphosed. If you squeeze and heat a rock for a few million years it can turn into a new kind of rock. Rocks and debris continue to pile in layers until pressure and heat change the underlying layers to form metamorphic rocks.
 Source: science-scene.org
Source: science-scene.org
What s more eroded rocks may continue to press and squeeze into sedimentary rocks as the transformations due to pressure and heat take place. Rock cycle prepared by the michigan department of environmental quality office of geological survey. What s more eroded rocks may continue to press and squeeze into sedimentary rocks as the transformations due to pressure and heat take place. Deep below the surface these rocks are exposed to high heat and pressure which change them into a different type of rock called metamorphic rock. If you squeeze and heat a rock for a few million years it can turn into a new kind of rock.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what is heat and pressure in the rock cycle by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.