What is stain in microbiology
What Is Stain In Microbiology. This procedure is called the hanging drop. Colouration of microorganisms by applying single dye to a fixed smear is termed simple staining. Gram staining helps to identify bacterial pathogens in specimens and cultures by their gram reaction gram positive and gram negative and morphology cocci rod. The use of selected dyes to colour biological specimens such as cells cell products thin slices of tissues or microorganisms to assist in examination and identification under the microscope.
 Staining In Microbiology Youtube From youtube.com
Staining In Microbiology Youtube From youtube.com
Colouration of microorganisms by applying single dye to a fixed smear is termed simple staining. One covers the fixed smear with stain for specific period after which this solution is washed off with water and slide blotted dry. The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. It was developed by danish microbiologist hans christian gram in 1884 as an effective method to distinguish between bacteria with different types of cell walls and even today it remains one of the most frequently used staining techniques. The microorganism is invisible to the naked eye therefore to make it visible the staining is performed which gives divergence to a microscopic image. Gram stain is a very important differential staining technique used in the initial characterization and classification of bacteria in microbiology.
The gram stain procedure is a differential staining procedure that involves multiple steps.
The gram stain procedure is a differential staining procedure that involves multiple steps. It was developed by danish microbiologist hans christian gram in 1884 as an effective method to distinguish between bacteria with different types of cell walls and even today it remains one of the most frequently used staining techniques. Stains work by increasing the contrast between different cellular components thereby highlighting specific cell structures. In preparation for staining a small sample of microorganisms is placed on a slide and permitted to air dry. The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. Both gram positive and gram negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls so initially all bacteria stain violet.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Both gram positive and gram negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls so initially all bacteria stain violet. The use of selected dyes to colour biological specimens such as cells cell products thin slices of tissues or microorganisms to assist in examination and identification under the microscope. Colouration of microorganisms by applying single dye to a fixed smear is termed simple staining. Stains are used commonly in microbiology to increase the contrast between microorganisms or parts of its and the background so that it can be easily visible. The smear is heat fixed by quickly passing it over a flame.
 Source: aem.asm.org
Source: aem.asm.org
The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. Simple staining makes the use of basic dyes like methylene blue safranin crystal violet malachite green etc. The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. The process of giving colour to particular organism or components of its is known as staining. Heat fixing kills the organisms makes them adhere to the slide and permits them to accept the stain.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. Collins dictionary of medicine robert m. The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. The gram stain procedure is a differential staining procedure that involves multiple steps. Stain or dye is the synthetic chemical which is derived from nitrobenzene or aniline.
 Source: biologyreader.com
Source: biologyreader.com
The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. The use of selected dyes to colour biological specimens such as cells cell products thin slices of tissues or microorganisms to assist in examination and identification under the microscope. The steps of. Both gram positive and gram negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls so initially all bacteria stain violet. Stains are chemical reagents or dye that imparts colour to cells and tissue sections of the biological specimens and aids in its visualization under a microscope.
 Source: bio.libretexts.org
Source: bio.libretexts.org
In preparation for staining a small sample of microorganisms is placed on a slide and permitted to air dry. Gram staining helps to identify bacterial pathogens in specimens and cultures by their gram reaction gram positive and gram negative and morphology cocci rod. The gram stain procedure is a differential staining procedure that involves multiple steps. The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. Stains are chemical reagents or dye that imparts colour to cells and tissue sections of the biological specimens and aids in its visualization under a microscope.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Heat fixing kills the organisms makes them adhere to the slide and permits them to accept the stain. Collins dictionary of medicine robert m. Colouration of microorganisms by applying single dye to a fixed smear is termed simple staining. The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. The gram stain involves staining bacteria fixing the color with a mordant decolorizing the cells and applying a counterstain.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents. Colouration of microorganisms by applying single dye to a fixed smear is termed simple staining. The gram stain involves staining bacteria fixing the color with a mordant decolorizing the cells and applying a counterstain. The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. Colouration of microorganisms by applying single dye to a fixed smear is termed simple staining. It was developed by danish microbiologist hans christian gram in 1884 as an effective method to distinguish between bacteria with different types of cell walls and even today it remains one of the most frequently used staining techniques. This procedure is called the hanging drop. See also gram negative gram positive.
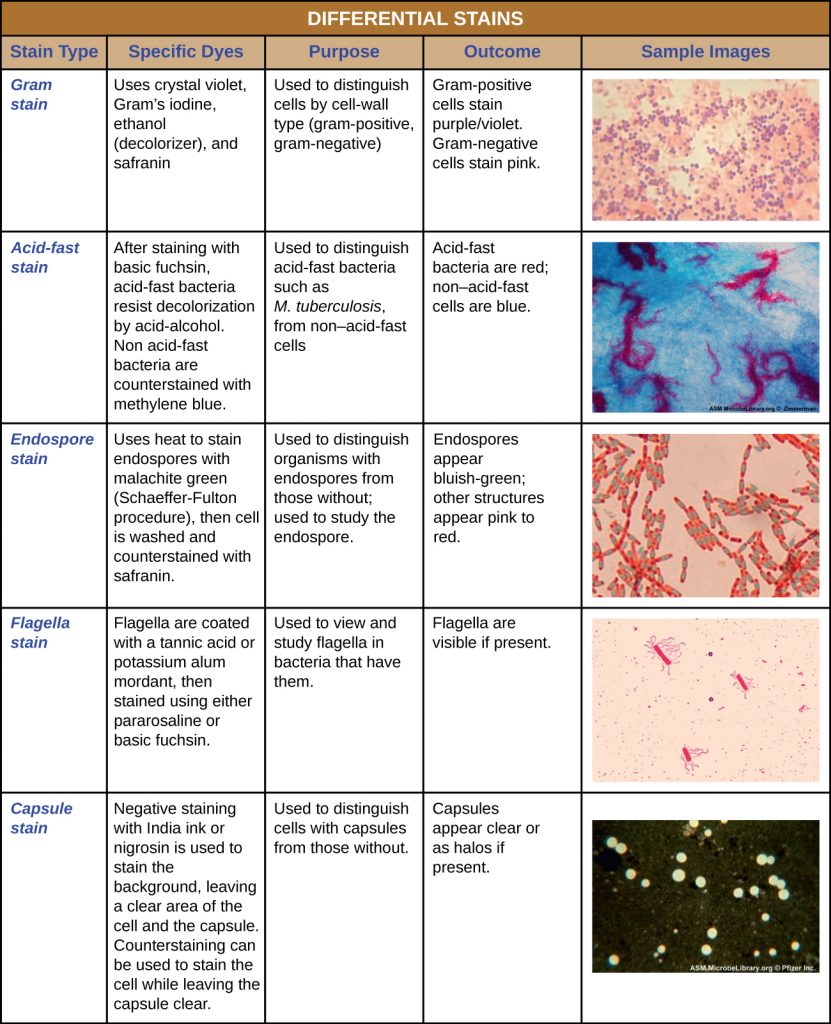 Source: ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub
Source: ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub
The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. Gram stain is a very important differential staining technique used in the initial characterization and classification of bacteria in microbiology. Both gram positive and gram negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls so initially all bacteria stain violet. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents. Gram staining helps to identify bacterial pathogens in specimens and cultures by their gram reaction gram positive and gram negative and morphology cocci rod.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
The process of giving colour to particular organism or components of its is known as staining. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents. The gram stain procedure is a differential staining procedure that involves multiple steps. Stains work by increasing the contrast between different cellular components thereby highlighting specific cell structures. Simple staining makes the use of basic dyes like methylene blue safranin crystal violet malachite green etc.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Stains are chemical reagents or dye that imparts colour to cells and tissue sections of the biological specimens and aids in its visualization under a microscope. One covers the fixed smear with stain for specific period after which this solution is washed off with water and slide blotted dry. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents. Gram stain is a very important differential staining technique used in the initial characterization and classification of bacteria in microbiology. The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Stain or dye is the synthetic chemical which is derived from nitrobenzene or aniline. Collins dictionary of medicine robert m. The smear is heat fixed by quickly passing it over a flame. This procedure is called the hanging drop. The use of selected dyes to colour biological specimens such as cells cell products thin slices of tissues or microorganisms to assist in examination and identification under the microscope.
 Source: microbiologynotes.org
Source: microbiologynotes.org
In preparation for staining a small sample of microorganisms is placed on a slide and permitted to air dry. Gram staining helps to identify bacterial pathogens in specimens and cultures by their gram reaction gram positive and gram negative and morphology cocci rod. Stains are used commonly in microbiology to increase the contrast between microorganisms or parts of its and the background so that it can be easily visible. Both gram positive and gram negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls so initially all bacteria stain violet. Collins dictionary of medicine robert m.
 Source: microbeonline.com
Source: microbeonline.com
Collins dictionary of medicine robert m. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents. In preparation for staining a small sample of microorganisms is placed on a slide and permitted to air dry. The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. The gram stain involves staining bacteria fixing the color with a mordant decolorizing the cells and applying a counterstain.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. The gram stain procedure is a differential staining procedure that involves multiple steps. One covers the fixed smear with stain for specific period after which this solution is washed off with water and slide blotted dry. In preparation for staining a small sample of microorganisms is placed on a slide and permitted to air dry. It was developed by danish microbiologist hans christian gram in 1884 as an effective method to distinguish between bacteria with different types of cell walls and even today it remains one of the most frequently used staining techniques.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title what is stain in microbiology by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.