What is the choroid
What Is The Choroid. Choroid is part of the uvea and supplies nutrients to the inner parts of the eye. In species with limited retinal vasculature e g horse rabbit guinea pig the retina depends to a large extent on the choroidal blood supply. Choriocapillaris stroma and lamina fusca. 1 the choroid provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer layers of the retina.
 Choroid Wikipedia From en.wikipedia.org
Choroid Wikipedia From en.wikipedia.org
The choroid is extremely vascular with its capillaries arranged in a single layer on the inner surface to nourish the outer retinal layers figure 11 14. The choroid plexus is part of the blood brain barrier that protects the central nervous system from harmful chemicals and is the primary source of the various components of cerebrospinal fluid. The choroid is the middle layer of the eye that contains blood vessels and connective tissue between the sclera the white of the eye and the retina at the back of the eye. The choroid is the vascular layer of the eye that lies between the retina and the sclera. Choroid noun the highly vascularised and pigmented nutrient middle layer of the eye located between retina and sclera the tapetum is an iridescent layer in the choroid of some eyes. Choriocapillaris stroma and lamina fusca.
1 the choroid provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer layers of the retina.
The choroid is the middle layer of the eye that contains blood vessels and connective tissue between the sclera the white of the eye and the retina at the back of the eye. The choroid is extremely vascular with its capillaries arranged in a single layer on the inner surface to nourish the outer retinal layers figure 11 14. It joins the ciliary body anteriorly and lies between the retina and sclera posteriorly. The vascular major blood vessel central layer of the eye lying between the retina and sclera. It contains the retinal pigmented epithelial cells and provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer retina. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear of the eye at 0 2 mm while in the outlying areas it narrows to 0 1 mm.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The vascular major blood vessel central layer of the eye lying between the retina and sclera. The choroid is a thin variably pigmented vascular tissue forming the posterior uvea. Within this section of the eye there are four different layers. The choroid is extremely vascular with its capillaries arranged in a single layer on the inner surface to nourish the outer retinal layers figure 11 14. Part of the uvea.
 Source: areaoftalmologica.com
Source: areaoftalmologica.com
The choroid plexus is part of the blood brain barrier that protects the central nervous system from harmful chemicals and is the primary source of the various components of cerebrospinal fluid. The choroid plexus or plica choroidea borders the membrane of the pia mater and the ventricles of the brain. The choroid plexus is part of the blood brain barrier that protects the central nervous system from harmful chemicals and is the primary source of the various components of cerebrospinal fluid. Its main purpose is to send oxygen and other nutrients to the retina. The choroid is thickest in the back of the eye where it is about 0 2 mm and narrows to 0 1 mm in the peripheral part of the eye.
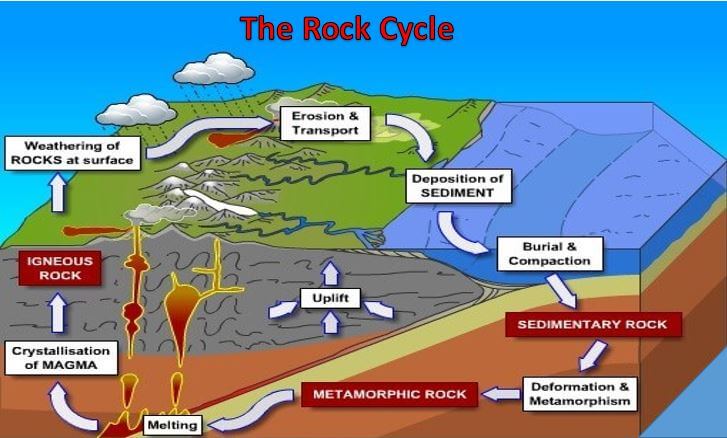
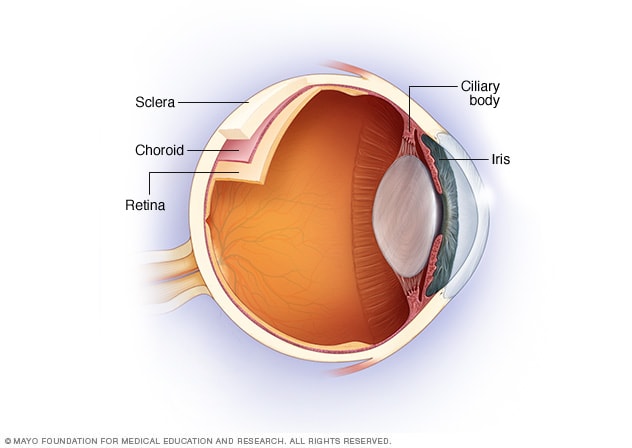 Source: mayoclinic.org
Source: mayoclinic.org
In species with limited retinal vasculature e g horse rabbit guinea pig the retina depends to a large extent on the choroidal blood supply. Its main purpose is to send oxygen and other nutrients to the retina. The choroid is the vascular layer of the eye that lies between the retina and the sclera. Within this section of the eye there are four different layers. In species with limited retinal vasculature e g horse rabbit guinea pig the retina depends to a large extent on the choroidal blood supply.
 Source: theeyepractice.com.au
Source: theeyepractice.com.au
Technically the choroid is the vascular part of the human eye that includes the connective tissue. Choroid is part of the uvea and supplies nutrients to the inner parts of the eye. The vascular major blood vessel central layer of the eye lying between the retina and sclera. The choroid is extremely vascular with its capillaries arranged in a single layer on the inner surface to nourish the outer retinal layers figure 11 14. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear of the eye at 0 2 mm while in the outlying areas it narrows to 0 1 mm.
Source: aao.org
The choroid is a thin variably pigmented vascular tissue forming the posterior uvea. Its function is to provide nourishment to the outer layers of the retina through blood vessels. The choroid is a thin variably pigmented vascular tissue forming the posterior uvea. Its main purpose is to send oxygen and other nutrients to the retina. Technically the choroid is the vascular part of the human eye that includes the connective tissue.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The choroid plexus or plica choroidea borders the membrane of the pia mater and the ventricles of the brain. The choroid also known as the choroidea or choroid coat is the vascular layer of the eye containing connective tissues and lying between the retina and the sclera. Choroid noun the highly vascularised and pigmented nutrient middle layer of the eye located between retina and sclera the tapetum is an iridescent layer in the choroid of some eyes. The choriocapillaris provides nutrients to the rpe and the outer third of the retina. Its main purpose is to send oxygen and other nutrients to the retina.
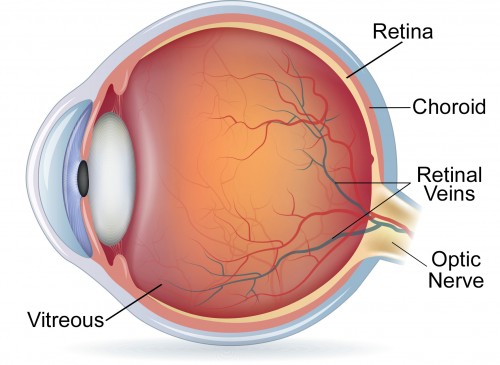 Source: vmrinstitute.com
Source: vmrinstitute.com
1 the choroid provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer layers of the retina. Its main purpose is to send oxygen and other nutrients to the retina. Technically the choroid is the vascular part of the human eye that includes the connective tissue. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear of the eye at 0 2 mm while in the outlying areas it narrows to 0 1 mm. Choroid noun the highly vascularised and pigmented nutrient middle layer of the eye located between retina and sclera the tapetum is an iridescent layer in the choroid of some eyes.
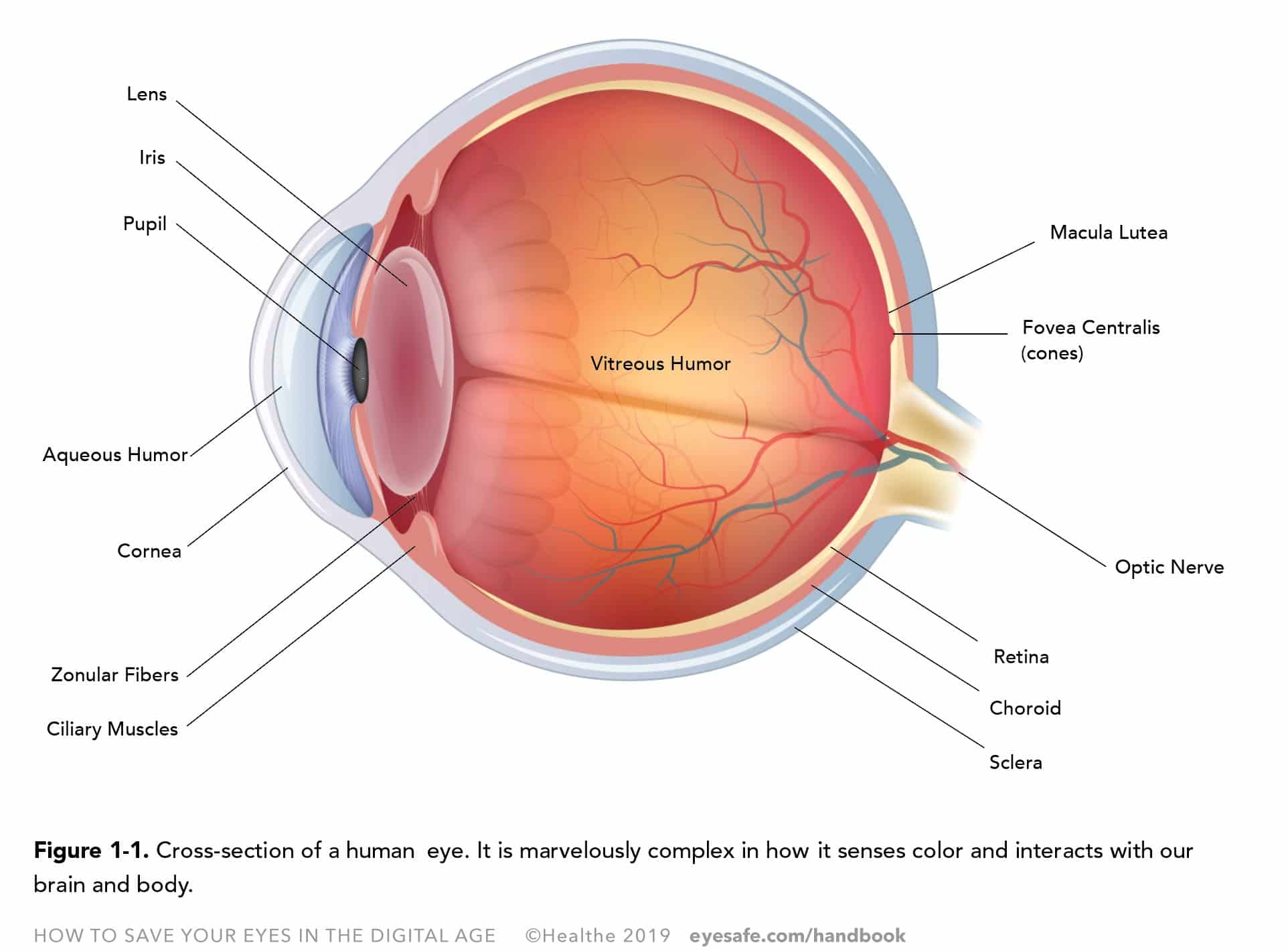 Source: eyesafe.com
Source: eyesafe.com
1 the choroid provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer layers of the retina. The choroid is the middle layer of the eye that contains blood vessels and connective tissue between the sclera the white of the eye and the retina at the back of the eye. It joins the ciliary body anteriorly and lies between the retina and sclera posteriorly. The choroid also known as the choroid coat or choroidea is located between the retina and sclera. Choroid is part of the uvea and supplies nutrients to the inner parts of the eye.
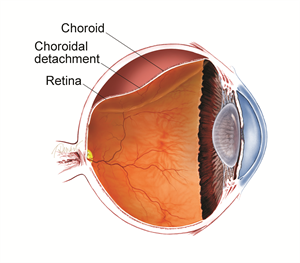 Source: asrs.org
Source: asrs.org
1 the choroid provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer layers of the retina. The choroid is the middle layer of the eye that contains blood vessels and connective tissue between the sclera the white of the eye and the retina at the back of the eye. It joins the ciliary body anteriorly and lies between the retina and sclera posteriorly. Its main purpose is to send oxygen and other nutrients to the retina. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear of the eye at 0 2 mm while in the outlying areas it narrows to 0 1 mm.
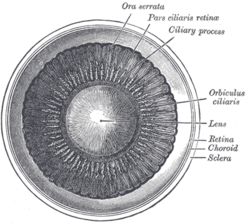 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The choroid is the vascular layer of the eye that lies between the retina and the sclera. The choroid also known as the choroid coat or choroidea is located between the retina and sclera. The choroid plexus or plica choroidea borders the membrane of the pia mater and the ventricles of the brain. The choroid is a thin pigmented vascular network consisting of three layers from inner to outer. Its main purpose is to send oxygen and other nutrients to the retina.
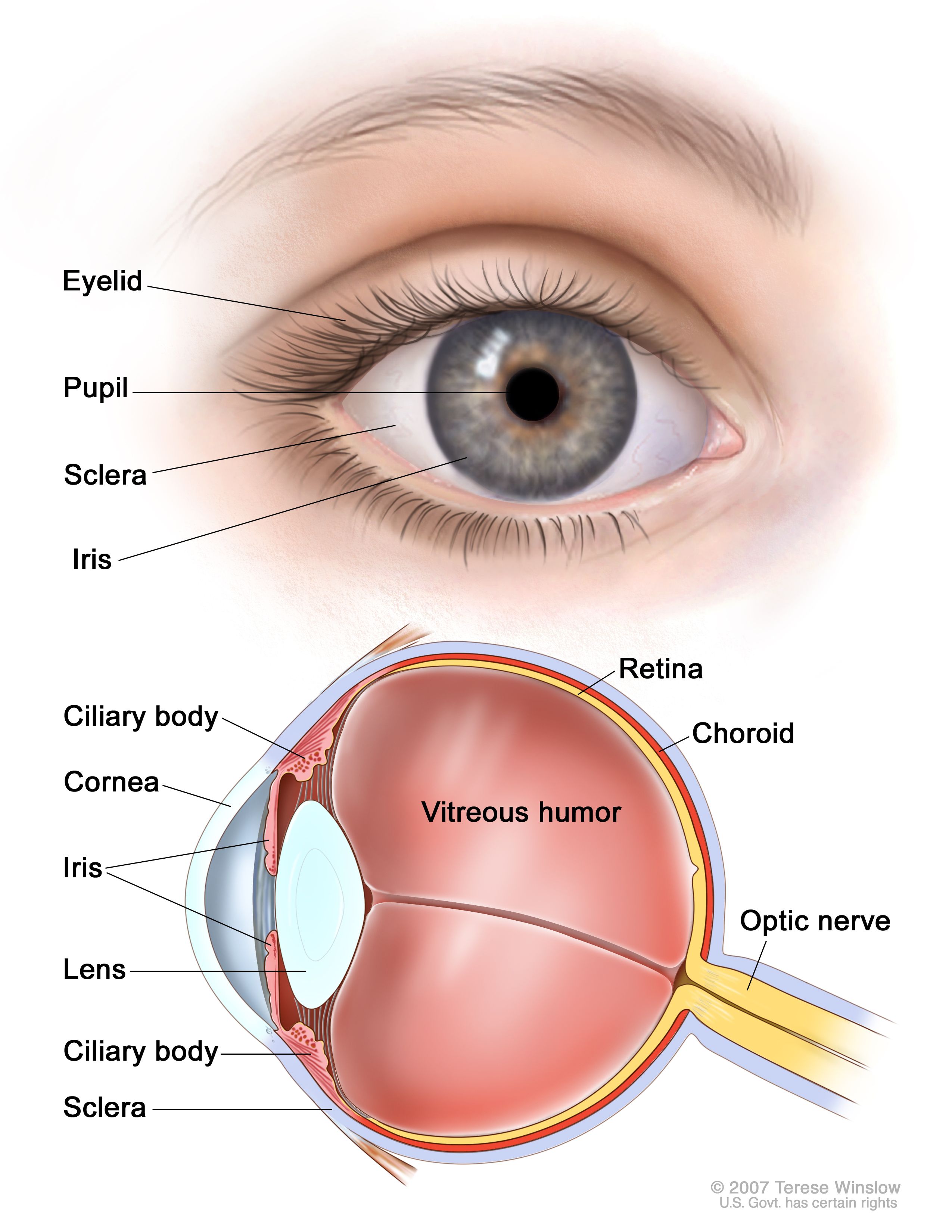 Source: cancer.gov
Source: cancer.gov
The choroid is thickest in the back of the eye where it is about 0 2 mm and narrows to 0 1 mm in the peripheral part of the eye. The choroid plexus or plica choroidea borders the membrane of the pia mater and the ventricles of the brain. It joins the ciliary body anteriorly and lies between the retina and sclera posteriorly. The choroid is the vascular layer of the eye that lies between the retina and the sclera. The choroid is extremely vascular with its capillaries arranged in a single layer on the inner surface to nourish the outer retinal layers figure 11 14.
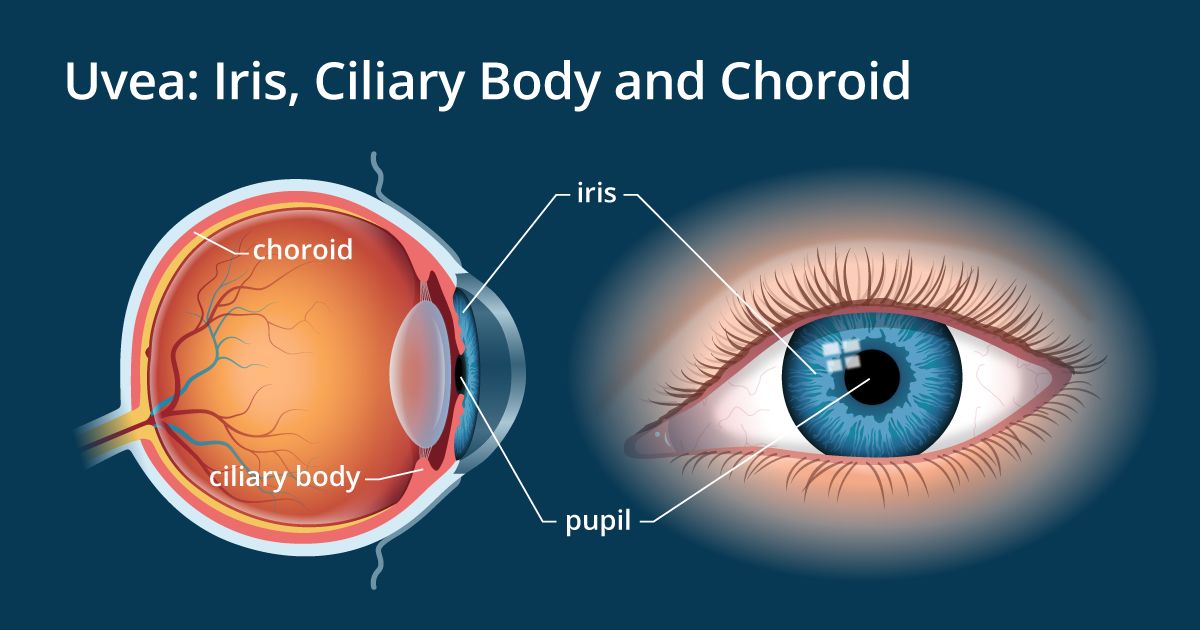 Source: allaboutvision.com
Source: allaboutvision.com
In species with limited retinal vasculature e g horse rabbit guinea pig the retina depends to a large extent on the choroidal blood supply. Choriocapillaris stroma and lamina fusca. In species with limited retinal vasculature e g horse rabbit guinea pig the retina depends to a large extent on the choroidal blood supply. Its function is to provide nourishment to the outer layers of the retina through blood vessels. It contains the retinal pigmented epithelial cells and provides oxygen and nourishment to the outer retina.
 Source: fightingblindness.ie
Source: fightingblindness.ie
The choroid also known as the choroidea or choroid coat is the vascular layer of the eye containing connective tissues and lying between the retina and the sclera. The choroid is thickest in the back of the eye where it is about 0 2 mm and narrows to 0 1 mm in the peripheral part of the eye. The choroid also known as the choroidea or choroid coat is the vascular layer of the eye containing connective tissues and lying between the retina and the sclera. It joins the ciliary body anteriorly and lies between the retina and sclera posteriorly. In species with limited retinal vasculature e g horse rabbit guinea pig the retina depends to a large extent on the choroidal blood supply.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The choroid is a thin variably pigmented vascular tissue forming the posterior uvea. Choroid noun the highly vascularised and pigmented nutrient middle layer of the eye located between retina and sclera the tapetum is an iridescent layer in the choroid of some eyes. The choroid is a thin pigmented vascular network consisting of three layers from inner to outer. The choroid is extremely vascular with its capillaries arranged in a single layer on the inner surface to nourish the outer retinal layers figure 11 14. The choroid is the vascular layer of the eye that lies between the retina and the sclera.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The choroid is the middle layer of the eye that contains blood vessels and connective tissue between the sclera the white of the eye and the retina at the back of the eye. The choroid is a thin variably pigmented vascular tissue forming the posterior uvea. Within this section of the eye there are four different layers. The choriocapillaris provides nutrients to the rpe and the outer third of the retina. It joins the ciliary body anteriorly and lies between the retina and sclera posteriorly.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what is the choroid by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.