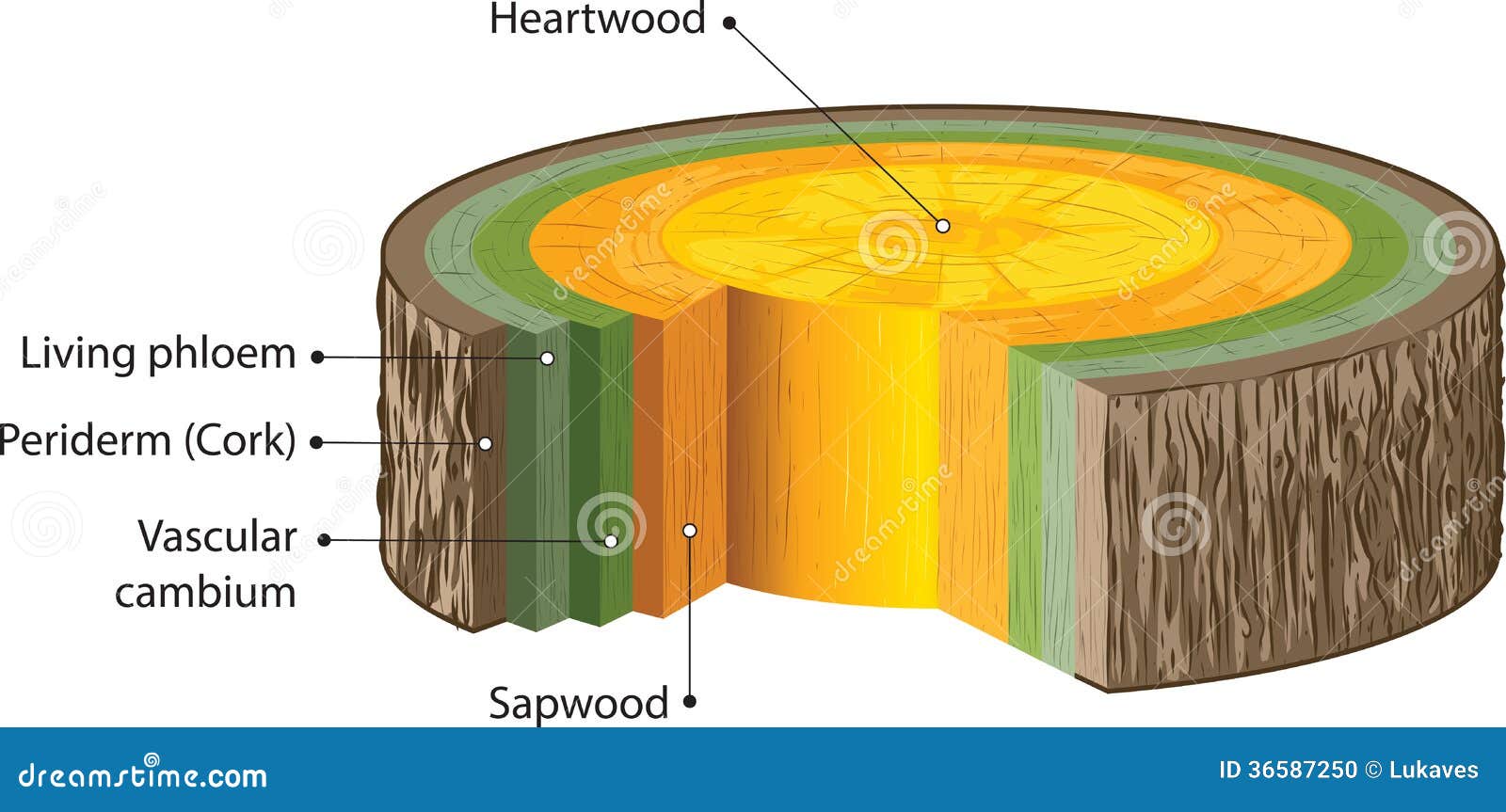
Woody stem diagram
Woody Stem Diagram. The upper diagram shows a young woody dicot stem before it has started to grow in width. 5 3 secondary growth and the anatomy of wood most monocots and many dicots show little or no secondary. Woody dicot stem. The sapwood is xylem that is still actively transporting and the heartwood is xylem that is lignified so is no longer active.
 Biology Anatomy And Function Of Woody Stems Unit 5 Diagram Quizlet From quizlet.com
Biology Anatomy And Function Of Woody Stems Unit 5 Diagram Quizlet From quizlet.com
Woody dicot stem. It increases the diameter of the stem. The sapwood is xylem that is still actively transporting and the heartwood is xylem that is lignified so is no longer active. In woody plants secondary tissues constitute the bulk of the. Roots stems and leaves diagrams. And non woody stem on diagram.
This diagram shows the layers of vascular tissue that make up a woody trunk or stem.
5 3 secondary growth and the anatomy of wood most monocots and many dicots show little or no secondary. Leaf cross section. The upper diagram shows a young woody dicot stem before it has started to grow in width. Secondary growth is the formation of secondary tissues from lateral meristems. The economic value of woody stems the functions and organization of the shoot system primary growth and stem anatomy primary tissues of dicot stems develop. Woody stem has the following parts moving from inside towards the outer side pith xylem for the transport of water and nutrients cambium phloem for the transport of food and organic nutrients and bark present outside cove.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
A section of rosemary stem an example of a woody plant showing a typical wood structure. Cork is critical in that it keeps out both biological and. Woody dicot cross section of the diagrams. External features of the stem. It increases the diameter of the stem.
 Source: cronodon.com
Source: cronodon.com
The cork cambium divides toward the edge to form the cork and towards the center to produce phelloderm cells. This set is often saved in the same folder as. Using the diagram below as a guide work through the slides images of woody sections from conifers and angiosperms. The economic value of woody stems the functions and organization of the shoot system primary growth and stem anatomy primary tissues of dicot stems develop. Woody stem has the following parts moving from inside towards the outer side pith xylem for the transport of water and nutrients cambium phloem for the transport of food and organic nutrients and bark present outside cove.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
5 3 secondary growth and the anatomy of wood most monocots and many dicots show little or no secondary. Leaf cross section. Roots stems and leaves diagrams. It increases the diameter of the stem. Learners can use microscopes or photomicrographs to observe and draw cross sections of the root and woody stems are harder than herbaceous stems.
 Source: www2.mcdaniel.edu
Source: www2.mcdaniel.edu
The sapwood is xylem that is still actively transporting and the heartwood is xylem that is lignified so is no longer active. And non woody stem on diagram. Leaf cross section. Woody stem has the following parts moving from inside towards the outer side pith xylem for the transport of water and nutrients cambium phloem for the transport of food and organic nutrients and bark present outside cove. In woody plants secondary tissues constitute the bulk of the.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
And non woody stem on diagram. Using the diagram below as a guide work through the slides images of woody sections from conifers and angiosperms. Cork is critical in that it keeps out both biological and. This diagram shows the layers of vascular tissue that make up a woody trunk or stem. This set is often saved in the same folder as.
 Source: cronodon.com
Source: cronodon.com
Woody stem has the following parts moving from inside towards the outer side pith xylem for the transport of water and nutrients cambium phloem for the transport of food and organic nutrients and bark present outside cove. External features of the stem. B diagram of a similar apex to more clearly show the umbrella shaped ptm. A woody plant is a plant that produces wood as its structural tissue and thus has a hard stem. This set is often saved in the same folder as.
 Source: alamy.com
Source: alamy.com
The sapwood is xylem that is still actively transporting and the heartwood is xylem that is lignified so is no longer active. This set is often saved in the same folder as. The sapwood is xylem that is still actively transporting and the heartwood is xylem that is lignified so is no longer active. External structure of a woody stem. The cork cambium divides toward the edge to form the cork and towards the center to produce phelloderm cells.
 Source: pinterest.nz
Source: pinterest.nz
Primary growth produces growth in length and development of lateral appendages. Cork is critical in that it keeps out both biological and. A section of rosemary stem an example of a woody plant showing a typical wood structure. This diagram shows the layers of vascular tissue that make up a woody trunk or stem. A woody plant is a plant that produces wood as its structural tissue and thus has a hard stem.
 Source: bio.miami.edu
Source: bio.miami.edu
A section of rosemary stem an example of a woody plant showing a typical wood structure. External root structure. Woody dicot stem. This diagram shows the layers of vascular tissue that make up a woody trunk or stem. 5 3 secondary growth and the anatomy of wood most monocots and many dicots show little or no secondary.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Woody dicot stem. Primary growth produces growth in length and development of lateral appendages. Learners can use microscopes or photomicrographs to observe and draw cross sections of the root and woody stems are harder than herbaceous stems. External features of the stem. External root structure.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Woody stem has the following parts moving from inside towards the outer side pith xylem for the transport of water and nutrients cambium phloem for the transport of food and organic nutrients and bark present outside cove. Learners can use microscopes or photomicrographs to observe and draw cross sections of the root and woody stems are harder than herbaceous stems. The economic value of woody stems the functions and organization of the shoot system primary growth and stem anatomy primary tissues of dicot stems develop. The sapwood is xylem that is still actively transporting and the heartwood is xylem that is lignified so is no longer active. The upper diagram shows a young woody dicot stem before it has started to grow in width.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A section of rosemary stem an example of a woody plant showing a typical wood structure. In woody plants secondary tissues constitute the bulk of the. Secondary growth is the formation of secondary tissues from lateral meristems. Roots stems and leaves diagrams. The upper diagram shows a young woody dicot stem before it has started to grow in width.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
Woody dicot stem. The upper diagram shows a young woody dicot stem before it has started to grow in width. Woody dicot stem. This diagram shows the layers of vascular tissue that make up a woody trunk or stem. External root structure.
 Source: mandevillehigh.stpsb.org
Source: mandevillehigh.stpsb.org
And non woody stem on diagram. The upper diagram shows a young woody dicot stem before it has started to grow in width. External structure of a woody stem. B diagram of a similar apex to more clearly show the umbrella shaped ptm. External root structure.
 Source: www2.palomar.edu
Source: www2.palomar.edu
In woody plants secondary tissues constitute the bulk of the. And non woody stem on diagram. Using the diagram below as a guide work through the slides images of woody sections from conifers and angiosperms. Secondary growth is the formation of secondary tissues from lateral meristems. Cork is critical in that it keeps out both biological and.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title woody stem diagram by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.